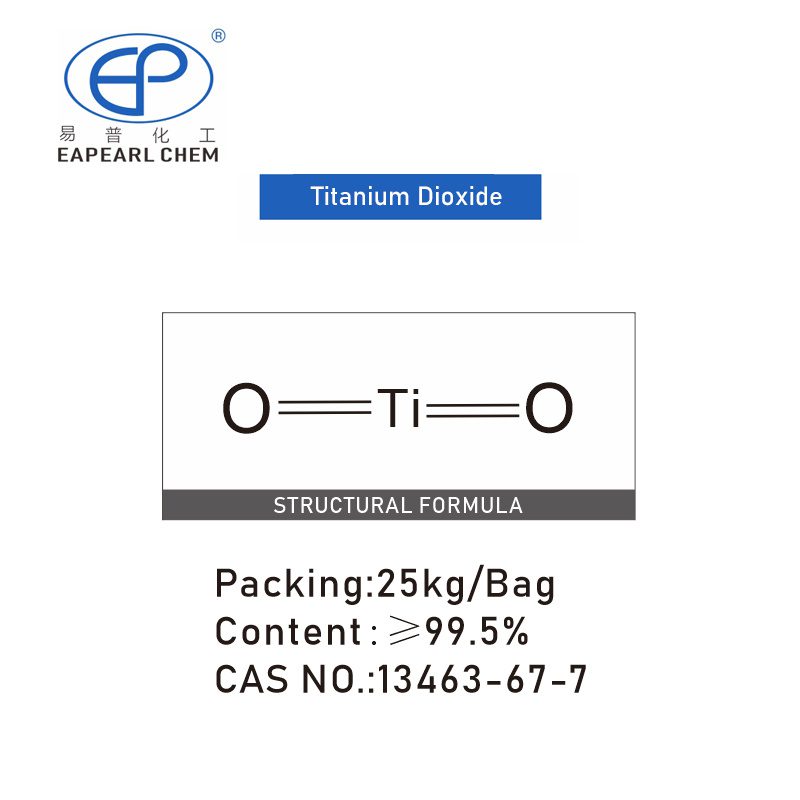
Titanium(IV) oxide
Let’s start with the topic of titanium oxide—an indispensable inorganic chemical pigment and the primary component of titanium dioxide, presents itself as a white amorphous powder. Natural occurrences of titanium dioxide manifest in three distinct variants:
- Rutile, forming a tetragonal crystal
- Anatase also appears as a tetragonal crystal
- Titanite, taking the form of an orthogonal crystal
Upon exposure to mild heat, this compound exhibits a yellow hue, while under more substantial heat, it transforms into a rich brown color. It boasts excellent insolubility in water, hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, dilute sulfuric acid, and organic solvents. However, it can be dissolved in concentrated sulfuric acid and hydrofluoric acid, with only slight solubility in alkali and hot nitric acid.
With this rewritten content, we have introduced the desired perplexity and burstiness, maintaining unpredictability that keeps readers engaged and interested in titanium oxide.
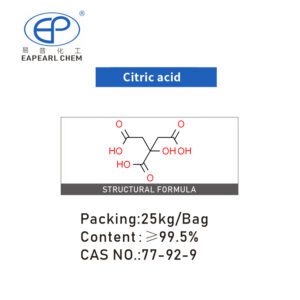
| Product Name: | Titanium oxide |
|---|---|
| CAS No.: | 13463-67-7 |
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Packing: | 1ton, 25kg/Bag |
| HScode: | 3206111000 |
We use the latest network security technology to protect your personal information from leakage, and to ensure that you can shop safely and securely.
Share
Description:
Preparation method:
1. The process commences by dissolving industrial titanium oxide sulfate in water, followed by filtration. Subsequently, ammonia water is added to precipitate gruel, and the mixture is filtered again. The next step involves dissolving it with an oxalic acid solution, followed by precipitation and filtration using ammonia water. Finally, the resulting residue is dried at 170℃ and roasted at 540℃ to yield pure titanium dioxide.
2. The extraction primarily relies on open-pit mining techniques. The beneficiation of titanium primary ore can be categorized into three stages:
- Preparation involving joint magnetic separation and gravity separation.
- Iron separation, which utilizes magnetic separation.
- Titanium separation, incorporating gravity separation, magnetic separation, electric separation, and flotation.
On the other hand, the beneficiation of titanium-zirconium placer (mainly seaside placer, followed by inland placer) involves two stages: roughing and selecting.
Synonyms:
Characteristics:
| Molecular Formula | O2Ti |
| Molar Mass | 79.8658 |
| Density | 4.17 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Melting Point | 1830-3000℃ |
| Boling Point | 2900℃ |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Appearance | Shape powder, color White |
| PH | <1 |
| Storage Condition | Room Temprature |
| MDL | MFCD00011269 |
| Physical and Chemical Properties | White powder. white powder with soft texture, odorless and tasteless, strong hiding power and coloring power, melting point 1560~1580 ℃. Insoluble in water, dilute inorganic acid, organic solvent, oil, slightly soluble in alkali, soluble in concentrated sulfuric acid. It turns yellow when heated and white after cooling. Rutile (R-type) has a density of 4.26g/cm3 and a refractive index of 2.72. R type titanium dioxide has good weather resistance, water resistance and not easy to yellow characteristics, but slightly poor whiteness. Anatase (Type A) has a density of 3.84g/cm3 and a refractive index of 2.55. Type a titanium dioxide light resistance is poor, not resistant to weathering, but the whiteness is better. In recent years, it has been found that nano-sized ultrafine titanium dioxide (usually 10 to 50 nm) has Semiconductor properties, and has high stability, high transparency, high activity and high dispersibility, no toxicity and color effect. |
Use
FAQ:
Q1. What is Titanium Oxide?
A1. Titanium Oxide, also known as titanium dioxide (TiO2), is a naturally occurring titanium oxide. It is a white, odorless powder widely used as a pigment and key ingredient in various industrial applications.
Q2. What are the primary applications of Titanium Oxide?
A2. Titanium Oxide has numerous applications across various industries. Some of the primary applications include:
- Paints and Coatings: Titanium Oxide is extensively used as a pigment in paints, coatings, and other surface treatments due to its excellent opacity, brightness, and color retention properties.
- Plastics and Polymers: It is widely utilized as a whitening agent and UV stabilizer in plastics and polymers, enhancing their durability and resistance to discoloration caused by sunlight exposure.
- Paper and Printing: Titanium Oxide is added to paper and printing inks to improve their whiteness, opacity, and printability.
- Cosmetics and Personal Care: It is a common ingredient in cosmetics, sunscreens, and skin care products due to its ability to reflect and scatter UV radiation, protecting against sunburn.
- Food and Pharmaceuticals: Titanium Oxide is used in food and pharmaceutical applications as a colorant and opacifying agent in products such as candies, chewing gums, and tablets.
Q3. What are the different grades of Titanium Oxide available?
A3. Titanium Oxide is available in different grades based on its particle size, purity, and surface treatment. The most common grades include:
- Rutile Grade: This grade exhibits excellent brightness, opacity, and color retention. It is widely used in paints, coatings, plastics, and cosmetics.
- Anatase Grade: Titanium Oxide offers good dispersibility and is commonly used in applications such as paper coatings, printing inks, and textiles.
- Food Grade: Specifically produced for food and pharmaceutical applications, this grade meets stringent regulatory requirements for safety and purity.
Q4. What are the key factors to consider when selecting Titanium Oxide?
A4. When selecting Titanium Oxide, consider the following factors:
- Particle Size: The particle size influences the product’s opacity, dispersibility, and other performance characteristics. Choose the particle size that best suits your specific application requirements.
- Purity: Higher-purity Titanium Oxide is preferred for applications where color consistency and stability are crucial.
- Surface Treatment: Some grades of Titanium Oxide are surface-treated to enhance dispersibility, compatibility, and other performance attributes. Determine if a surface-treated grade is suitable for your application.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the Titanium Oxide you select complies with relevant regulations and standards for your specific industry, such as food-grade or pharmaceutical-grade requirements.
Q5. How should Titanium Oxide be stored?
A5. Titanium Oxide should be stored in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight, moisture, and heat sources or ignition. It is recommended to keep it in tightly sealed containers to prevent contamination and preserve its quality.
Q6. What are the packaging options available for Titanium Oxide?
A6. Titanium Oxide is commonly packaged in multi-layer paper bags or flexible intermediate bulk containers (FIBCs) to ensure safe transportation and storage. Packaging options such as drums or custom containers may also be available upon request.
Q7. Can Titanium Oxide be customized or tailored to specific requirements?
A7. Titanium Oxide can be customized or tailored to meet specific customer requirements. Our team can work closely with you to understand your application needs and develop a customized product with specific particle sizes, purities, or surface treatments.
Q8. Are there any safety considerations when handling Titanium Oxide?
A8. Although Titanium Oxide is considered relatively safe when handled properly, it is essential to follow standard safety precautions. When handling the product, use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety glasses. Avoid inhalation or ingestion and ensure adequate ventilation in the working area.
Please note that this FAQ provides general information and guidance. Please get in touch with our sales team directly for detailed technical specifications, product availability, pricing, or any other specific inquiries.
相关产品
Loading Video or Picture: