Dimethylformamide (DMF)
Discover the Pinnacle of Purity and Efficiency with Eapearl's Dimethylformamide (NMF)
Unlock the Potential of Superior-Quality NMF for Your Industrial Needs
What Dimethylformamide (DMF) Is
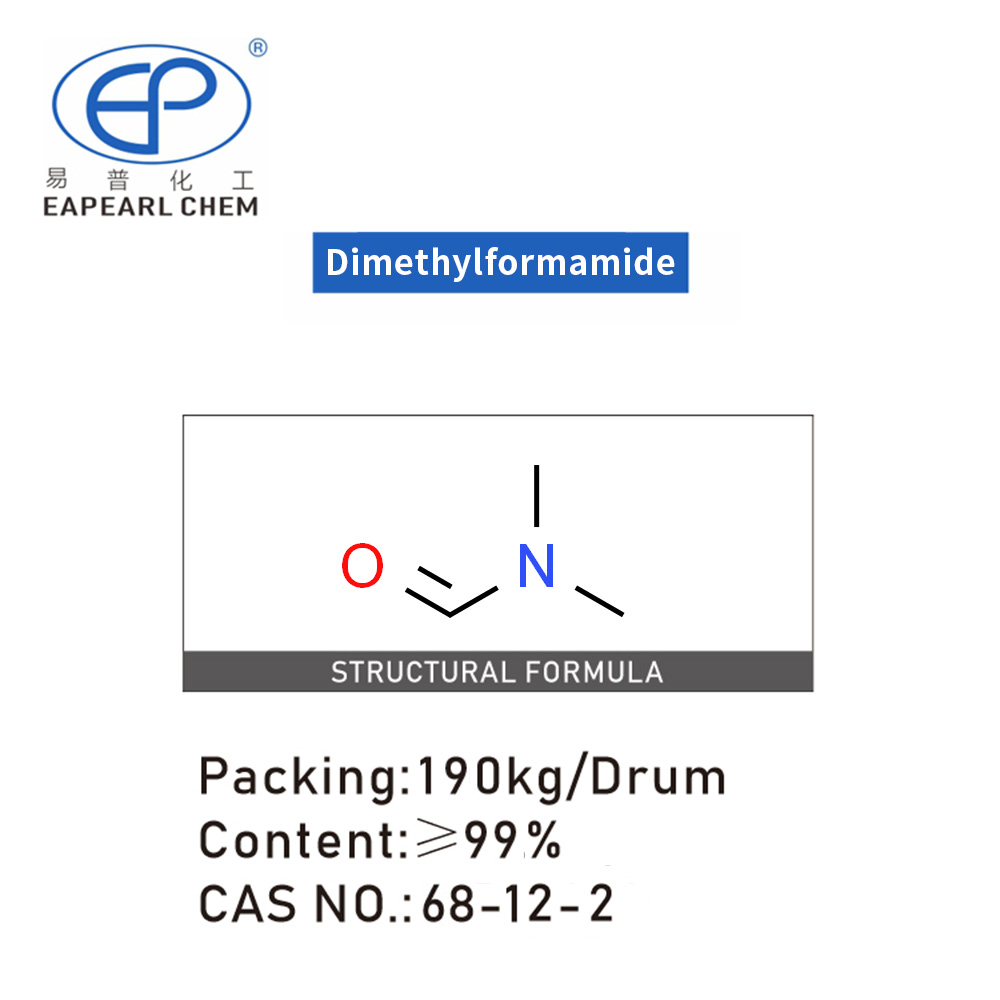

Dimethylformamide, often termed DMF, is a versatile organic compound widely recognized in various industrial applications due to its unique chemical properties. Chemically known as N, N-Dimethylformamide, this compound belongs to the amide class and is characterized by the formula C₃H₇NO.
Nature and Properties
DMF is a colorless, water-miscible liquid with a faint, amine-like odor. It is a polar solvent with high solubility in water, making it an essential solvent in chemical reactions. The compound has a boiling point of 153 °C and a melting point of -61 °C. Due to its aprotic nature, it does not donate protons in chemical reactions. This characteristic significantly enhances its utility in various chemical synthesis processes.
Synonyms
DMF; Formdimethylamide; Dimethyl Formamide; Formyldimethylamine; N,N-Dimethylformamide; N,N-dimethyl-Formamide; Dimethylamidkyselinymravenci; Amide,n,n-dimethyl-formicaci.
Safety and Environmental Impact
While DMF is invaluable in industrial applications, it is essential to handle it with care due to its potential health hazards. It can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Proper safety measures, including protective equipment and adequate ventilation, are essential when handling DMF. Environmental considerations are also crucial, as DMF can pose risks to aquatic life and should be disposed of responsibly.
Dimethylformamide (DMF) Packaging Information


Metal Drum


IBC Drum


Flexible Bag


ISO Tank
| Cyclohexanone packaging | Capacity | 20GP | 40GP |
| drum | 190 kg /drum | total 80 drums, Net 15.2 ton | total 120 drums, Net 22.8 ton |
| IBC drum | 1000 kg /IBC | total 20 IBC, Net 20 ton | total 24 IBC, Net 24 ton |
| ISO Tank | 23 ton /ISO Tank | 1 ISO Tank, Net 23 ton | N/A |
For Dimethylformamide (DMF), we welcome you to test and check the quality, if you need a sample please contact our sales team to discuss your sample requirements, we believe that our product quality is suitable for the specific application. We provide samples free of charge but the shipping cost will be borne by you.
The Applications of Dimethylformamide (DMF)

Pharmaceutical Industry
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) Synthesis: DMF is extensively used as a solvent in synthesizing APIs. Its ability to dissolve many materials makes it ideal for facilitating chemical reactions that produce complex pharmaceutical compounds.
Peptide Synthesis: In peptide synthesis, DMF is used as a solvent due to its compatibility with the amino acid components and ability to enhance reaction rates.
Extraction Solvent: DMF is employed in extraction processes to purify and isolate pharmaceutical compounds, efficiently separating desired elements from complex mixtures.
Chemical Manufacturing
Production of Acrylic Fibers and Plastics:DMF is a critical solvent in producing acrylic fibers. It effectively dissolves polymers, which are then spun into fibers used in textiles. In plastics manufacturing, DMF acts as a solvent in polymerization, producing high-quality plastics.
Solvent in Paints and Coatings: Due to its solvency power and evaporation rate, DMF is used in formulating various paints and coatings, enhancing their application properties and finish quality.



Electronics Industry
– Circuit Board Production: For circuit board manufacturing, DMF is used in the photolithography process, where it dissolves photoresists. This is essential for creating accurate and intricate designs on circuit boards, which are critical for the functioning of electronic devices.
– Electronic Component Fabrication: In fabricating electronic components like capacitors, DMF’s role is to dissolve and stabilize the dielectric materials and other chemicals, ensuring the components’ precise composition and consistent quality.
Agricultural Sector
– Pesticide Formulation: DMF’s application in pesticide formulation involves dissolving active ingredients to create effective pest control solutions. Its ability to enhance the absorption of these chemicals by plants ensures improved efficacy of the pesticides, contributing to better crop protection.



Adhesive and Ink Production
– Manufacturing of Adhesives: DMF is instrumental in adhesive manufacturing due to its ability to dissolve various polymers and resins, creating adhesives with optimal viscosity, adhesion properties, and durability for multiple applications.
– Ink Production: DMF is valued for its quick-drying properties and ability to dissolve complex dyes and pigments in ink production. This results in inks consistent in color, fast-drying, and suitable for various printing applications, including industrial and commercial printing.
Solvent for Chemical Reactions
– Organic Synthesis: In organic synthesis, DMF provides a stable medium for various reactions, including condensation, hydrolysis, and polymerization. Its inert nature means it does not interfere with the reaction mechanisms, making it an ideal solvent for synthesizing a wide array of organic compounds.
– Catalysis and Reagent Solvent: DMF is often used as a solvent in catalytic processes, particularly in reactions involving transition metal catalysts. Its ability to solubilize both the catalyst and reactants significantly enhances the efficiency and selectivity of the reactions.



Research and Development
– Analytical and Laboratory Use: In research laboratories, DMF is frequently used in analytical procedures, such as spectroscopy and chromatography, due to its compatibility with various analytical techniques. It is also a common solvent in chemical research and development, aiding in synthesizing and analyzing new chemical compounds.
Production Technology of Dimethylformamide (DMF)
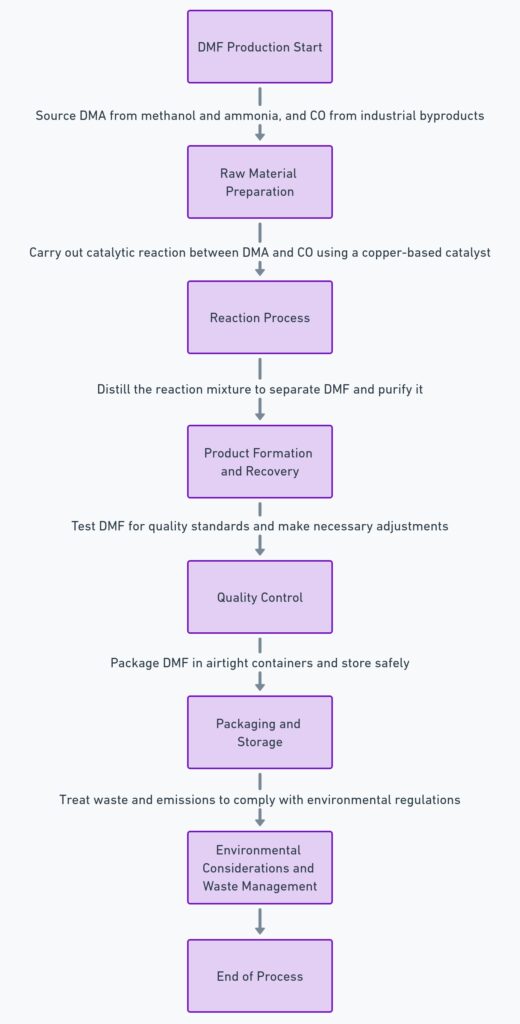

Dimethylformamide (DMF) production is a well-established industrial process, typically involving the reaction of dimethylamine with carbon monoxide under specific conditions. Here’s a detailed overview of the typical production process:
1. Raw Material Preparation
– Dimethylamine (DMA): Sourced as a primary raw material, typically obtained from the reaction of methanol and ammonia.
– Carbon Monoxide (CO): A key reactant, usually derived as a byproduct from various industrial processes or specifically synthesized for this purpose.
2. Reaction Process
– Catalytic Reaction: The production of DMF involves a catalytic reaction between dimethylamine and carbon monoxide. This reaction is usually carried out in the presence of a catalyst, such as a copper-based catalyst, to enhance efficiency and yield.
– Reactor Conditions: The reaction typically occurs in a specialized reactor under controlled temperature and pressure conditions. The temperature is usually maintained around 100-180°C, and the pressure is kept at a range that facilitates the reaction while ensuring safety.
3. Product Formation and Recovery
– Reaction Mixture: The reaction produces a mixture containing DMF, unreacted dimethylamine, and other byproducts.
– Separation: The mixture is then distilled to separate DMF from other components. This involves heating the mixture and collecting the DMF with a specific boiling point (153°C at atmospheric pressure).
– Purification: The distilled DMF may undergo further purification to remove any remaining impurities. This can involve additional distillation steps, filtration, or other purification methods.
4. Quality Control
– Testing: Samples of the produced DMF are tested to ensure they meet quality standards. Parameters such as purity, moisture content, and the presence of impurities are checked against industry specifications.
– Adjustments: If necessary, adjustments to the process are made to ensure the final product consistently meets the required quality standards.
5. Packaging and Storage
– Packaging: The purified DMF is packaged for storage and distribution. It is typically stored in airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption and degradation.
– Safety Measures: Given DMF’s hazardous nature, it is handled and stored with strict safety protocols, including using appropriate containment and labeling as per regulatory standards.
6. Environmental Considerations and Waste Management
– Effluent Treatment: Any waste or effluent generated during production is treated to neutralize harmful components before disposal.
– Emission Control: To comply with environmental regulations, steps are taken to minimize and treat emissions, especially carbon monoxide.
How can we handle your order?


step 1
We will communicate with you within 24 hours after you send an enquiry.


step 2
If you need sample testing, we will send samples within 5 days,≤50kg, Express delivery recommended, usually called as DDU service; delivery time 5-7 days. Door to door service.


step 3
If you need bulk goods after the sample test is qualified, we will ship the goods to the port and keep the samples within 6 days after the order is confirmed. Sea shipping recommended, usually called as FOB, CFR, or CIF service.delivery time 10-45 days. Port to port service.


step 4
After waiting for you to receive the goods, we will arrange professional staff to pay a return visit within 7 days.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Dimethylformamide (DMF) Technical Data
| Name | N,N-Dimethylformamide |
| Molecular Formula | C3H7NO |
| Molar Mass | 73.09 |
| Density | 0.944 g/mL (lit.) |
| Melting Point | -61 °C (lit.) |
| Boling Point | 153 °C (lit.) |
| Specific Rotation(α) | 0.94 º |
| Flash Point | 136°F |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Solubility | water: miscible |
| Vapor Presure | 2.7 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| Vapor Density | 2.5 (vs air) |
| Appearance | liquid |
| Color | APHA: ≤15 |
| Odor | Faint, ammonia-like odor detectable at 100 ppm |
| Exposure Limit | NIOSH REL: TWA 10 ppm (30 mg/m3), IDLH 500 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 10ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 10 ppm (adopted). |
| Maximum wavelength(λmax) | λ: 270 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 275 nm Amax: 0.30λ: 295 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 310 nm Amax: 0.05λ: 340-400 nm Amax: |
| Merck | 143243 |
| BRN | 605365 |
| pKa | -0.44±0.70(Predicted) |
| PH | 7 (200g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Storage Condition | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Explosive Limit | 2.2-16%(V) |
| Refractive Index | n20/D 1.430(lit.) |
| Physical and Chemical Properties | Density 0.945 melting point -61°C boiling point 153°C refractive index 1.429-1.432 flash point 58°C specific rotation 0.94 ° water-soluble solution |
Qualifications and Documents of DMF
DMF Safety and Handling Information
Dimethylformamide (DMF) is a volatile organic compound with extensive applications in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to chemical manufacturing. Due to its environmental and health impacts, proper storage and disposal of DMF are crucial. This article outlines the best practices for storing DMF and disposing of it in an environmentally responsible manner.
Storage of Dimethylformamide (DMF)
General Storage Guidelines
– Container Material: DMF should be stored in chemically resistant containers, typically made of stainless steel or certain types of plastic like polyethylene.
– Temperature Conditions: It is advisable to store DMF at a cool, stable temperature, away from direct sunlight and heat sources to prevent degradation and evaporation.
– Ventilation: Storage areas should be well-ventilated to prevent the accumulation of fumes, which can be hazardous.
– Segregation: DMF should be stored separately from incompatible substances, such as strong acids, oxidizing agents, and bases.
Safety Measures
– Leak Prevention: Regular checks for leaks and container integrity are essential to prevent environmental contamination and health hazards.
-Labeling and Documentation: Containers should be clearly labeled with readily available material safety data sheets (MSDS) outlining handling and first aid measures.
Environmental Disposal of DMF
Regulatory Compliance
Disposal of DMF must comply with local and international environmental regulations. These regulations typically mandate the treatment of DMF waste to reduce its environmental impact.
Disposal Methods
– Incineration: Controlled incineration, wherein DMF is burnt at high temperatures, is common. This process should be carried out with emission control measures to handle releasing toxic gases.
– Chemical Treatment: DMF can be chemically neutralized using treatment agents before disposal. This process transforms DMF into less harmful substances.
– Wastewater Treatment: When DMF is present in wastewater, specialized treatment processes are needed to remove it before the water is discharged into the environment. This often involves biological treatment processes or advanced oxidation processes.
Handling Spills and Leaks
In case of spills or leaks, containing and cleaning up DMF promptly is essential while following safety protocols. Absorbent materials like sand or vermiculite can be used, and the contaminated material must then be disposed of as hazardous waste.
Environmental Impact
Toxicity
DMF is classified as a potential human carcinogen and poses significant risks to aquatic life. It is essential to prevent its release into water bodies and soil.
Emission Control
During both storage and disposal processes, controlling the emission of DMF into the atmosphere is crucial due to its contribution to air pollution and potential health hazards.
Conclusion
The storage and disposal of Dimethylformamide require careful consideration and adherence to safety and environmental standards. By implementing appropriate storage practices and disposal methods, the risks associated with DMF can be significantly mitigated, ensuring environmental safety and public health protection. Compliance with regulatory requirements is a legal obligation and a responsibility towards sustainable environmental stewardship.
Advantages of the Chinese DMF Market
China’s chemical industry has been rapidly growing, and a significant segment of this growth is attributed to the production and distribution of Dimethylformamide (DMF), a versatile organic solvent. The Chinese DMF market holds several competitive advantages in the global chemical industry landscape.
1. Large-Scale Production
CapacityChina is one of the world’s largest producers of DMF. Its massive production capacity is driven by numerous large-scale DMF manufacturing facilities. These facilities utilize advanced technologies that enhance production efficiency and output quality, ensuring a steady supply to meet domestic and international demands.
2. Cost-Effective Manufacturing
One of the key advantages of the Chinese DMF market is its cost-effectiveness. The availability of raw materials at relatively low prices and affordable labor costs contribute to reduced overall production expenses. This cost advantage allows Chinese DMF to be competitively priced globally.
3. Strategic Position for Global Trade
China’s strategic location with well-established maritime and land trade routes offers easy access to key global markets. The extensive port infrastructure facilitates efficient export operations, making shipping DMF to various international destinations convenient.
4. Diversified Industrial Applications
DMF is used in a variety of industrial applications, including the production of pharmaceuticals, acrylic fibers, plastics, pesticides, and adhesives. The versatility of its applications ensures a consistent demand within multiple industrial sectors, adding to the market’s stability and growth.
5. Innovation and Research
Chinese chemical companies invest significantly in research and development, focusing on innovative production methods and environmental sustainability. This investment in R&D has led to advancements in DMF production techniques, making processes more environmentally friendly and efficient.
6. Robust Domestic Market
The domestic demand for DMF in China is strong, driven by its widespread use across several industries, including pharmaceuticals, textiles, and electronics. This robust internal market provides a stable base for DMF producers and less reliance on international market fluctuations.
7. Compliance with International Standards
Chinese DMF manufacturers adhere to stringent quality control protocols and international standards. This compliance ensures the global acceptance of Chinese DMF, fostering trust among international buyers.
8. Government Policies and Support
The Chinese government’s supportive policies towards the chemical sector, including subsidies and tax incentives, have positively impacted the DMF industry. Such policies encourage production, innovation, and export activities.
9. Environmental Management
In response to global environmental concerns, China is progressively adopting stricter ecological regulations in chemical manufacturing. This shift towards more sustainable practices improves the international perception of Chinese chemicals, including DMF.
Conclusion
The Chinese DMF market, with its large-scale production, cost-effectiveness, strategic global trade position, diverse industrial applications, commitment to innovation, and adherence to international standards, stands as a strong contender in the worldwide chemical industry. These advantages position China as a leading DMF supplier and a key influencer in the global supply chain dynamics for this essential solvent.
Dimethylformamide (DMF) FAQs
Yes, purchasing and handling DMF typically requires qualifications and permits, as it is classified as a hazardous chemical. Regulatory bodies in many countries mandate that businesses taking DMF must comply with specific safety and environmental regulations. This includes obtaining permits, maintaining proper storage facilities, and ensuring that personnel handling DMF are adequately trained in hazardous material management and safety procedures. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to ensure DMF’s safe and responsible use.
Dimethylformamide (DMF) is an organic compound extensively used as a solvent in various industrial applications. It is a colorless liquid miscible with water and most organic solvents. Chemically, it is an amide derived from formic acid, characterized by the formula C₃H₇NO.
DMF finds diverse applications due to its excellent solvent properties. It’s commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce synthetic leathers, fibers, films, and surface coatings. Additionally, DMF is a critical solvent in manufacturing pesticides, pharmaceuticals, and acrylic fibers.
Yes, DMF has a distinct, slightly amine-like odor. However, it’s important to note that the odor threshold for DMF is relatively high. It may only be detectable once concentrations are above recommended exposure limits.
DMF can exhibit basic properties due to its aprotic nature. It can stabilize anions, making it useful in various chemical reactions, including organometallic reactions and acid-catalyzed processes.
Purchased from Eapearl, a reputable supplier known for its commitment to purity and compliance with safety and environmental standards. Eapearl offers reliable distribution, expert guidance, and tailored DMF solutions to meet various industrial needs. Contact Eapearl for more information or to place an order.
Yes, DMF and Ethyl Acetate are miscible in all proportions. This property is beneficial in applications requiring the dissolution of various organic compounds, as it allows for the creation of custom solvent mixtures with specific properties.
DMF is produced through the catalytic reaction of dimethylamine and carbon monoxide under high pressure and temperature. This process requires careful monitoring and control to ensure the purity and quality of the product.
Drying DMF involves using molecular sieves or desiccants like calcium hydride or barium oxide. These substances absorb water from DMF, reducing its moisture content to trace levels. The process must be conducted with care to avoid contamination and ensure moisture removal.
DMF should be balanced for safe disposal using chemical processes that convert it into less harmful substances. This often involves a reaction with strong acids or bases, followed by neutralization. The resulting mixture should be disposed of by local environmental regulations, ideally through a certified chemical waste disposal service.
DMF, DMSO (Dimethyl Sulfoxide), THF (Tetrahydrofuran), and DCM (Dichloromethane) differ in their chemical properties and applications. DMF is less volatile than DCM and has a higher boiling point than THF, making it suitable for applications requiring stable and high-boiling solvents. Unlike DMSO, DMF is more effective in facilitating specific chemical reactions due to its aprotic nature.


