1-Butanol
Discover the Unmatched Quality and Versatility of Our 1-Butanol
Your One-Stop Solution for High-Purity 1-Butanol – Where Safety and Performance Meet
In the bustling world of industrial solvents and chemical precursors, 1-Butanol stands out for its unparalleled purity and versatility. Whether you’re pushing the boundaries of research or spearheading the next big innovation in manufacturing, our 1-Butanol is the key ingredient your projects have been missing.
Quality and Specifications Unveiled
Dive into the specifics that define our 1-Butanol’s superiority. With unmatched purity levels, our 1-Butanol ensures your processes run smoothly and efficiently. It’s not just about meeting standards; it’s about exceeding them. Every batch is a testament to our commitment to excellence, offering you the specifications required for cutting-edge applications.
Your Applications, Our Solutions
Discover the myriad of ways our clients have harnessed the power of 1-Butanol across industries. From enhancing paint formulations to pioneering new biofuels, our 1-Butanol is the secret behind countless success stories. Learn how compatibility and performance intersect in our product, making it the go-to solution for innovators worldwide.
Ensuring Uninterrupted Supply
In a world where timing is everything, depend on us for reliable 1-Butanol supply. Our streamlined logistics and robust inventory ensure that your operations never skip a beat. Explore our flexible purchasing options, including bulk purchase discounts, tailored to keep your projects on track without breaking the bank.
End your search for a high-quality, versatile chemical solution with our premium 1-Butanol. From unparalleled purity to comprehensive support, discover how our 1-Butanol can revolutionize your industry applications. Act now and join the ranks of innovators who choose nothing but the best for their projects.


Introduction
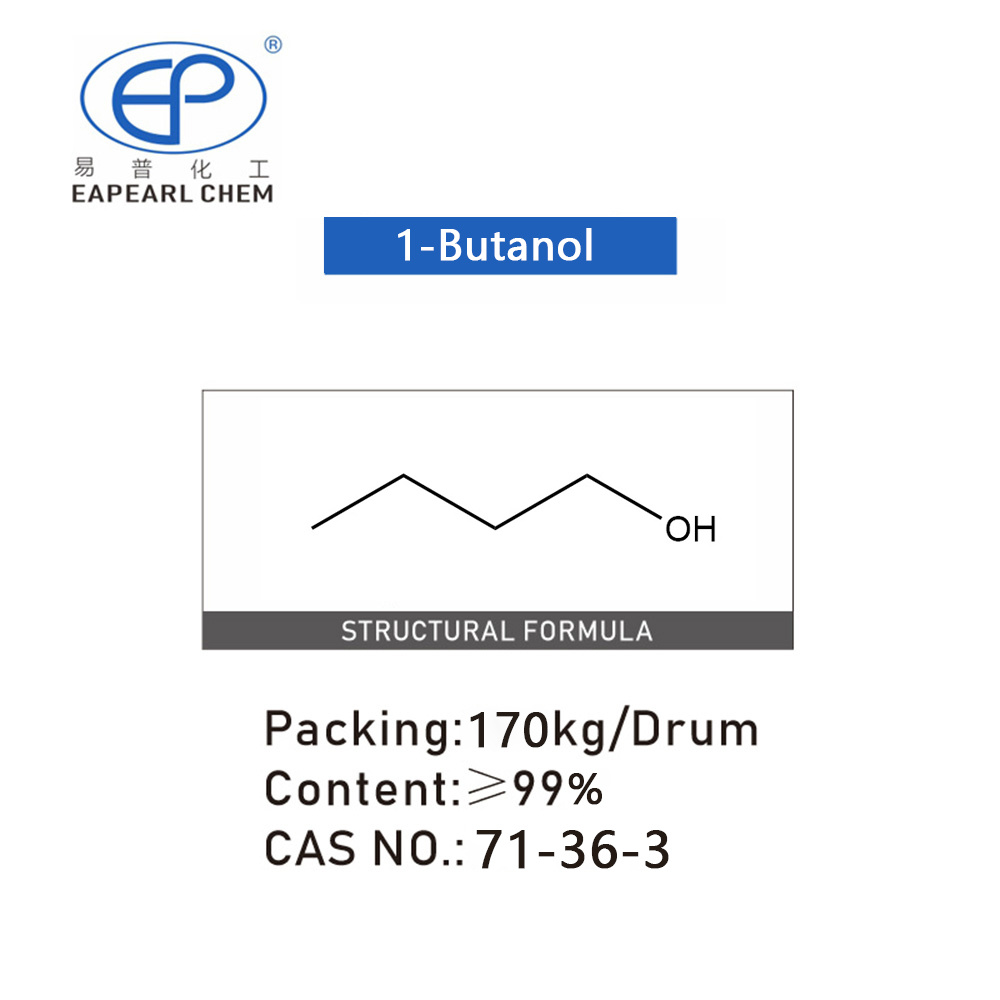
1-Butanol, commonly referred to as n-Butanol, butyl alcohol, or n-Butyl alcohol, is a four-carbon linear alcohol with the chemical formula C4H9OH. This organic compound is notable for its role in various industrial applications due to its solvent properties and medium volatility. 1-Butanol is a colorless liquid under ambient conditions, presenting a characteristic alcoholic odor. It is produced in significant quantities for use in a wide range of chemical processes and applications. The compound’s versatility and safety profile make it a valuable resource across numerous sectors.
synonyms
Butyl Alcohol, N-Butanol, Butanol, butanols, Butanol-1, butan-1-ol, Normal Butanol, n-butyl alcohol, Butyric alcohol, Natural Butyl Alcohol
Nature and Properties
1-Butanol exhibits a boiling point of approximately 117.7°C and a melting point of -89.8°C, characteristics that influence its handling and storage requirements. Its solubility in water and miscibility with organic solvents such as ethanol and ether make it an excellent solvent for various chemical syntheses and formulations. The substance is also known for its moderate toxicity, necessitating proper safety precautions during use.
Table of Contents
1-Butanol Packaging Information









| 1-Butanol Packaging | Capacity | 20GP | 40GP |
| drum | 170 kg /drum | total 80 drums, Net 13.6 ton | total 148 drums, Net 25.16 ton |
| IBC drum | 860 kg /IBC | total 20 IBC, Net 17.2 ton | total 30 IBC, Net 25.8 ton |
| ISO Tank | 20.5 ton /ISO Tank | 1 ISO Tank, Net 20.5 ton | N/A |
For 1-Butanol, we welcome you to test and check the quality, if you need a sample please contact our sales team to discuss your sample requirements, we believe that our product quality is suitable for the specific application. We provide samples free of charge but the shipping cost will be borne by you.
Applications of 1-Butanol
1-Butanol, a versatile organic solvent with a wide range of industrial and commercial uses, plays a pivotal role in various sectors due to its unique chemical properties. Below are the detailed applications of 1-Butanol in different fields:
Industrial Solvent
1-Butanol is extensively used as a solvent in the manufacturing of paints, coatings, inks, and adhesives. Its ability to dissolve both polar and non-polar substances makes it exceptionally versatile. In paint formulations, 1-Butanol reduces viscosity and improves flow, enabling smoother application and finish. In the production of adhesives, it enhances the solubility of synthetic resins, improving adhesive properties and drying times.






Chemical Intermediate
As a chemical intermediate, 1-Butanol serves as a precursor in the synthesis of butyl acrylate, a fundamental component in water-based adhesives and acrylic fibers. Butyl acrylate offers excellent adhesion and durability, making it ideal for coatings and textiles. Additionally, 1-Butanol is used in the production of butyl acetate, a solvent in the manufacturing of plastics and synthetic fibers, and in the creation of pharmaceuticals, showcasing its role in complex chemical syntheses.
Biofuel Component
The potential of 1-Butanol as a biofuel component has garnered attention due to its higher energy content compared to ethanol, making it a more efficient fuel alternative. Its compatibility with existing gasoline engines and infrastructure, without modifications, positions it as a promising renewable energy source. Research focuses on producing 1-Butanol through fermentation processes, highlighting its sustainability and reduced environmental impact compared to fossil fuels.






Extraction Agent
In the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries, 1-Butanol is utilized as an extraction agent due to its selective solubility properties. It efficiently extracts essential oils, flavors, and fragrances from natural sources, ensuring the purity and concentration of these valuable components. This application is critical in the production of high-quality cosmetics, perfumes, and pharmaceuticals, where ingredient purity is paramount.
Cleaning Agent
The cleaning industry benefits from 1-Butanol’s effectiveness as a degreasing agent in industrial and laboratory settings. Its ability to dissolve organic materials makes it ideal for cleaning surfaces contaminated with oils, fats, and waxes. Additionally, 1-Butanol is used in electronic and precision equipment cleaning, where residue-free results are essential for maintaining functionality and performance.





Plasticizers
In manufacturing plasticizers, 1-Butanol reacts with acids (e.g., phthalic anhydride, acrylic acid) to form esters like dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and butyl acrylate. These esters, added to PVC, enhance plastic flexibility and softness, improving materials for use in cables, flooring, toys, and medical devices.
The diverse applications of 1-Butanol across various industries underscore its importance as a chemical solvent, intermediate, and potential sustainable fuel. Its role in enhancing product formulations, contributing to renewable energy solutions, and facilitating complex chemical processes demonstrates the compound’s versatility and value to industrial, environmental, and commercial endeavors. If you have any questions about the application of 1-Butanol, please contact our team of experts.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
The Dangers and Safety Precautions of 1-Butanol
Flammability and Fire Risk
The relatively low flash point of 1-Butanol, approximately 35°C (95°F), means that even at room temperature, it can easily become volatile, forming vapors that can ignite if exposed to an ignition source such as sparks, open flames, or even hot surfaces. This property necessitates stringent safety measures in environments where 1-Butanol is used, stored, or transported.
Toxicity of 1-Butanol
1-Butanol’s toxicity is moderate compared to other alcohols. It can cause irritation to the skin, eyes, and respiratory tract upon exposure. Inhalation of high concentrations can lead to central nervous system depression, manifesting as dizziness, headaches, nausea, and in severe cases, unconsciousness. Chronic exposure might lead to more serious health issues, including liver and kidney damage.
Comparison with Ethanol and Methanol:
- Ethanol is generally considered safer than 1-Butanol, with a lower toxicity profile making it suitable for consumption in beverages. However, excessive intake can lead to alcohol poisoning and long-term health effects.
- Methanol is significantly more toxic than both 1-Butanol and ethanol. Even small amounts of methanol can be fatal if ingested, inhaled, or absorbed through the skin, as it metabolizes into formaldehyde and formic acid, which are highly toxic to the central nervous system and internal organs.
Toxicity Information
1-Butanol is less toxic than methanol but more toxic than ethanol. Its moderate toxicity requires that exposures be carefully managed to avoid adverse health effects. The primary concerns with 1-Butanol exposure include its potential to irritate mucous membranes and its depressive effects on the central nervous system.
Safety Precautions
Handling, Storing, and Disposing of 1-Butanol:
- Ventilation: Ensure good ventilation in areas where 1-Butanol is used to prevent vapor accumulation.
- Protective Equipment: Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and protective clothing, to prevent skin and eye contact. Use respirators in areas with poor ventilation.
- Storage: Store 1-Butanol in a cool, well-ventilated area away from heat sources and ignition points. Use containers that are tightly closed to prevent evaporation.
- Disposal: Dispose of 1-Butanol and its containers in accordance with local environmental regulations to minimize environmental impact.
Emergency Procedures:
- Spills: In case of a spill, use inert absorbent materials and ventilate the area. Avoid ignition sources.
- First Aid: For skin or eye contact, rinse thoroughly with water. If ingested or inhaled in high concentrations, seek immediate medical attention.
Adopting these safety precautions can significantly reduce the risks associated with handling and exposure to 1-Butanol, ensuring a safer working environment.
1-Butanol as a Potential Fuel: Pros and Cons
1-Butanol holds promise as a biofuel due to its chemical properties, which offer several advantages over traditional biofuels like methanol and ethanol. However, its use as a fuel also faces certain challenges that limit its widespread adoption.
1-Butanol as a Potential Fuel
Advantages:
- Energy Content: 1-Butanol has a higher energy content than ethanol and methanol, making it a more efficient fuel. Its energy density is closer to that of gasoline, which means it can deliver comparable mileage for vehicles without significant modifications.
- Lower Volatility: Compared to ethanol and methanol, 1-Butanol is less volatile. This results in lower evaporation losses and a reduced risk of vapor lock in engines, a problem often associated with ethanol in high temperatures.
- Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure: 1-Butanol can be blended with gasoline in higher concentrations than ethanol without separating in the presence of water or requiring modifications to existing fuel distribution systems. This makes it a more versatile and convenient option for blending with traditional fuels.
- Reduced Corrosiveness and Toxicity: It is less corrosive than ethanol and methanol, posing fewer risks to existing engines and fuel systems. Additionally, 1-Butanol is less toxic and biodegrades more readily than methanol, reducing environmental and health risks in case of spills.
Disadvantages:
- Production Costs: Currently, the production cost of 1-Butanol is higher than that of ethanol and methanol, primarily due to the more complex fermentation and refining processes required. This makes it less economically competitive as a biofuel.
- Lower Fuel Economy than Gasoline: Despite its higher energy content relative to ethanol and methanol, 1-Butanol still has a lower energy density than gasoline, which can lead to a decrease in fuel economy when used in high concentrations in fuel blends.
- Limited Production Capacity: The industrial production of 1-Butanol as a biofuel is not yet at a scale that can compete with ethanol or methanol, partly due to limited feedstock availability and the need for more advanced biotechnological processes.
Comparison with Methanol and Ethanol
- Efficiency: 1-Butanol’s higher energy content means it is more efficient than both methanol and ethanol, providing a better range for vehicles per gallon.
- Safety: Methanol is significantly more toxic and presents greater health risks in case of exposure. Ethanol and 1-Butanol are less toxic, but 1-Butanol’s lower volatility makes it safer to handle and store.
- Environmental Impact: All three alcohols are biodegradable, but 1-Butanol’s production and use emit fewer pollutants than methanol. Compared to ethanol, 1-Butanol offers similar environmental benefits, including lower greenhouse gas emissions than fossil fuels, but with the added advantage of being less hydroscopic, reducing the risk of water contamination.
Viability as a Biodiesel
As a biodiesel component, 1-Butanol has potential due to its compatibility with existing diesel engines and its ability to blend with diesel fuel without significant modifications. However, its current production cost and limited availability pose challenges to its viability as a widespread biodiesel option. Ongoing research into more cost-effective production methods and feedstock sources may enhance its feasibility in the future.
Conclusion
1-Butanol presents a promising but currently underutilized option in the biofuel landscape. Its advantages in terms of efficiency, safety, and compatibility with existing infrastructure position it as a strong candidate for future fuel applications. However, overcoming the economic and production scale challenges is crucial for 1-Butanol to become a viable alternative to conventional fuels and current biofuels like methanol and ethanol.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Technical Data of 1-Butanol
| Name | 1-Butanol |
| Synonyms | Butyl Alcohol, N-Butanol, Butanol, butanols, Butanol-1, butan-1-ol, Normal Butanol, n-butyl alcohol, Butyric alcohol, Natural Butyl Alcohol |
| CAS | 71-36-3 |
| EINECS | 200-751-6 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H10O |
| Molar Mass | 74.12 |
| Density | 0.81 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| Melting Point | -90 °C (lit.) |
| Boling Point | 116-118 °C (lit.) |
| Flash Point | 95°F |
| JECFA Number | 85 |
| Water Solubility | 80 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Vapor Presure | 6.7 hPa (20 °C) |
| Vapor Density | 2.55 (vs air) |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Color | APHA: ≤10 |
| Odor | Alcohol-like; pungent; strong; characteristic; mildly alcoholic, non residual. |
| Exposure Limit | TLV-TWA 300 mg/m3 (100 ppm) (NIOSH),150 mg/m3 (50 ppm) (ACGIH); IDLH 8000ppm (NIOSH). |
| Maximum wavelength(λmax) | λ: 215 nm Amax: 1.00λ: 220 nm Amax: 0.50λ: 240 nm Amax: 0.10λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.04λ: 280-400 nm Amax: |
| Merck | 141,540 |
| BRN | 969148 |
| pKa | 15.24±0.10(Predicted) |
| PH | 7 (70g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Storage Condition | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| Stability | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents, aluminium, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, copper, copper alloys. Flammable. |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Explosive Limit | 1.4-11.3%(V) |
| Refractive Index | n20/D 1.399(lit.) |
| MDL | MFCD00002902 |
| Physical and Chemical Properties | Characteristics of colorless liquid, with the taste of alcohol. |
| melting point -90.2 ℃ | |
| boiling point 117.7 ℃ | |
| relative density 0.8109 | |
| refractive index 1.3993 | |
| flash point 35~35.5 ℃ | |
| solubility at 20 ℃ solubility in water 7.7% by weight, the solubility of water in n-butanol was 20.1% by weight. Miscible with ethanol, ether and other organic solvents. | |
| HS Code | 2905 13 00 |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 4.36 g/kg (Smyth) |
| LogP | 0.88 |
1-Butanol Production
The production of 1-Butanol can be achieved through various methods, with the two primary routes being the petrochemical-based process and the fermentation process. Below, both methods are detailed, showcasing the intricacies and considerations of each production pathway.
Petrochemical-Based Production
Hydroformylation of Propylene (Oxo Process)
The petrochemical route, specifically the hydroformylation of propylene (also known as the Oxo Process), is a widely used method for producing 1-Butanol. This process involves several key steps:
Hydroformylation: Propylene is reacted with synthesis gas (a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen) in the presence of a catalyst (typically a complex of rhodium or cobalt) to produce butanal (butyraldehyde).
CH3CH=CH2+CO+H2→CH3CH2CH2CHO
Hydrogenation: The butanal produced in the hydroformylation step is then hydrogenated to yield 1-Butanol. This step also involves a catalyst, often based on nickel, palladium, or platinum, which facilitates the addition of hydrogen to the aldehyde group, converting it into an alcohol group.
CH3CH2CH2CHO+H2→CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
This petrochemical process is favored for its ability to produce large volumes of 1-Butanol efficiently. However, it depends on non-renewable fossil fuels, which has driven interest in more sustainable methods.
Fermentation Process
ABE Fermentation (Acetone-Butanol-Ethanol)
The fermentation process, known as ABE fermentation, is an alternative, more sustainable route to produce 1-Butanol. This biological process utilizes microorganisms, typically strains of the bacterium Clostridium, to convert carbohydrates (such as sugars from corn or molasses) into a mixture of solvents, including acetone, butanol, and ethanol.
Fermentation: The process begins with the preparation of a feedstock, which is a carbohydrate-rich substrate. The substrate is sterilized to remove any unwanted microbes and then inoculated with a culture of Clostridium. Under anaerobic conditions, the bacteria ferment the sugars in the feedstock, producing a mixture of solvents, including acetone, butanol, and ethanol, along with other by-products.
Recovery and Purification: The solvent mixture is then subjected to a series of separation and purification steps, such as distillation, to isolate 1-Butanol. Given the relatively low concentration of 1-Butanol in the fermentation broth (typically around 1-2% by volume), this step is crucial and can be energy-intensive.
The fermentation process for producing 1-Butanol is attractive due to its use of renewable resources and potential for lower carbon emissions. However, challenges such as the low productivity of the fermentation process and the high cost of separating 1-Butanol from the fermentation broth have limited its commercial scalability compared to the petrochemical route.
Conclusion
Both the petrochemical-based and fermentation processes for producing 1-Butanol have their advantages and limitations. The choice between these methods depends on factors such as cost, availability of feedstock, and environmental considerations. While the petrochemical route offers efficiency and scale, the fermentation process holds promise for sustainability and the use of renewable resources. Ongoing research and development efforts aim to improve the efficiency and reduce the costs associated with the fermentation production of 1-Butanol, making it a more viable alternative in the future.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Advantages of the Chinese 1-Butanol Market
The global 1-Butanol market is witnessing significant growth, with China emerging as a key player in this expansive trend. As of 2021, the market size for 1-Butanol was estimated to be substantial, with expectations to achieve remarkable growth by 2028, exhibiting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.5% from 2021 to 2028, as analyzed by ChemAnalyst Research.
Key Growth Drivers
Surge in Industrial Solvent Demand
A driving force behind the 1-Butanol market’s growth is the increased demand for industrial solvents. 1-Butanol’s application across diverse industries such as paints, coatings, adhesives, and pharmaceuticals, buoyed by economic improvements and industrial advancements, is expected to propel market expansion through 2028.
Critical Role in Chemical Synthesis
1-Butanol serves as a critical raw material in the synthesis of various chemicals, including plasticizers and butyl acrylate, accounting for a significant share of the chemicals used in these processes. Its indispensable role highlights the potential for sustained growth in the 1-Butanol sector.
China’s Market Advantages
Innovation and Production Capabilities
China’s focus on innovation, backed by extensive manufacturing capabilities, lays a robust foundation for the 1-Butanol industry’s growth. With substantial government support and a strong manufacturing base, China is set to continue its upward trajectory in the global 1-Butanol market.
Global Impact
China’s strategic positioning in the 1-Butanol market not only caters to domestic demands but also significantly influences global supply chains. Offering competitive pricing and a diverse product range, China stands as a pivotal exporter in the global 1-Butanol landscape.
Future Outlook
The future of the 1-Butanol market in China is poised for continued growth and expansion. The integration of 1-Butanol into various industrial processes, combined with China’s manufacturing prowess and market adaptability, indicates a dynamic and prosperous future for the 1-Butanol sector. With ongoing advancements and the strategic importance of 1-Butanol in chemical synthesis and industrial applications, the market is expected to thrive, reinforcing China’s key role in shaping the global dynamics of the 1-Butanol industry.
Our Team
FAQs of 1-Butanol
1-Butanol, also known as n-Butanol or butyl alcohol, is a four-carbon alcohol with the chemical formula C4H9OH. It’s used as a solvent, in chemical synthesis, and potentially as a biofuel due to its energy content.
To purchase 1-Butanol, buyers must confirm their qualifications for handling dangerous chemicals. This typically includes industries, research institutions, and professionals with a permit for hazardous material handling.
Purchasers need to provide evidence of their capability to safely store, handle, and dispose of hazardous chemicals. This includes a valid hazardous materials (HazMat) handling certificate, compliance with local safety regulations, and appropriate storage facilities.
1-Butanol is widely used as an industrial solvent, chemical intermediate (e.g., in the production of butyl acrylate and butyl acetate), and has potential as a biofuel due to its higher energy content compared to ethanol.
Proper safety measures include wearing protective gear, ensuring adequate ventilation, and storing 1-Butanol in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from ignition sources. Always refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) for detailed safety guidelines.
Yes, 1-Butanol is classified as a flammable liquid and can be harmful if inhaled, ingested, or it comes into contact with skin. It requires careful handling and storage in compliance with safety regulations.
Absolutely. We offer 100g-200g samples, with the client only covering shipping costs.
Standard lead times are approximately 2-4 weeks, varying based on order size and destination.
Our standard payment terms include a 30% advance and the balance against delivery, but terms can be negotiated for long-term partnerships.
Yes, we offer comprehensive after-sales support, addressing any post-purchase queries or concerns.
As a supplier, in order to provide you with an accurate quote for your product, please inform us of the quantity you require, the required purity specifications, any specific packaging needs, your shipping location, and whether your application requires any customization requirements or certifications.




