There have been many incidents of injuries due to accidental ingestion. One notable case involved a 2-year-old boy who lived with his grandparents. One day, the boy accidentally ingested caustic soda, mistaking it for sugar.By the time his grandmother noticed, his entire mouth was severely burned and blackened. In a panic, she tried to rinse his mouth with water, which worsened the situation, causing burns to spread to his mouth, stomach, legs, and any skin the caustic soda touched.The boy was rushed to a children’s hospital for emergency treatment. While his vital signs stabilized after medical intervention, the damage to his tissues and organs required prolonged surgical treatment and recovery.
Similar incidents are frequently reported. The common causes are usually caregiver negligence, insufficient knowledge about caustic soda, and improper handling.
A concerning misconception is that some people believe caustic soda and soda ash (sodium carbonate) are the same substance.
So, what exactly are caustic soda and soda ash, and what are their uses?
Simply put:Soda ash, or sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃), though called an “alkali,” is chemically a salt. Caustic soda, or sodium hydroxide (NaOH), is a true water-soluble strong alkali with strong corrosiveness and high hygroscopicity.Despite both being alkaline, they have significant differences in properties, uses, and safety.
This article delves into the characteristics and application areas of these two alkaline substances to help better understand their differences and promote their scientific application.
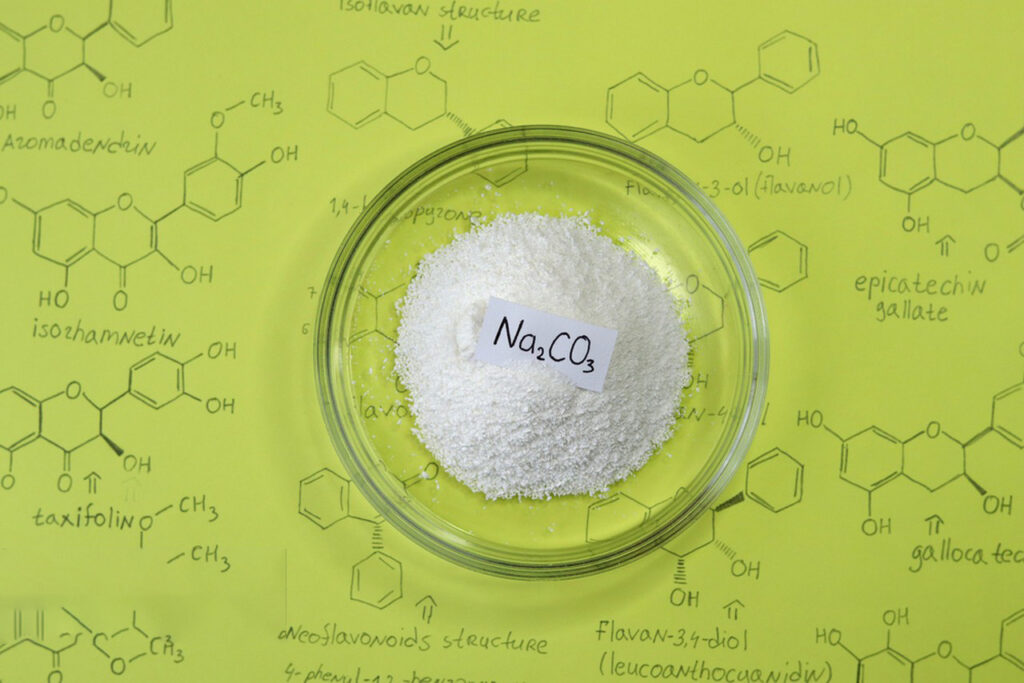




Caustic Soda: industrial -grade strong alkali
Caustic soda, also known as fire -alkali, its chemical name is sodium hydroxide (NaOH), composed of sodium (Na) and hydroxide (OH) ions, which is a white solid with strong corrosiveness, which is easy to dissolve in water and releases a lot of heat. At room temperature, it appears as white crystals, easily dissolving in water to form an alkaline solution. Sodium Hydroxide is a fundamental chemical raw material, widely used in various industries such as aluminum oxide production, papermaking, dyeing, chemical fibers, water treatment, metal refining, petroleum refining, cotton fabric processing, coal tar purification, food processing, wood processing, and the machinery and chemical industries.


However, caustic soda has strong irritation and corrosiveness, which will cause serious damage to the human body and the environment. Therefore, when using caustic soda, it is necessary to strictly abide by safety operating procedures to prevent accidents.
Soda Ash: food grade weak alkali
Soda Ash (Sodium Carbonate),composed of sodium (Na), carbon (C), and oxygen (O) ions,commonly known as edible alkali or washing soda, is a sodium salt of carbonic acid. It appears as a white, water-soluble salt.It has the generality and thermal stability of salt, which is easily soluble in water, and its aqueous solution is alkaline.

In the food industry, soda ash is used as a leavening agent, neutralizer, and fermenting agent in the production of foods such as steamed buns, noodles, and biscuits, making them softer and crisper. Additionally, edible alkali can be used for cleaning kitchen utensils and washing clothes, providing effective decontamination and grease removal. It is widely used in daily life.
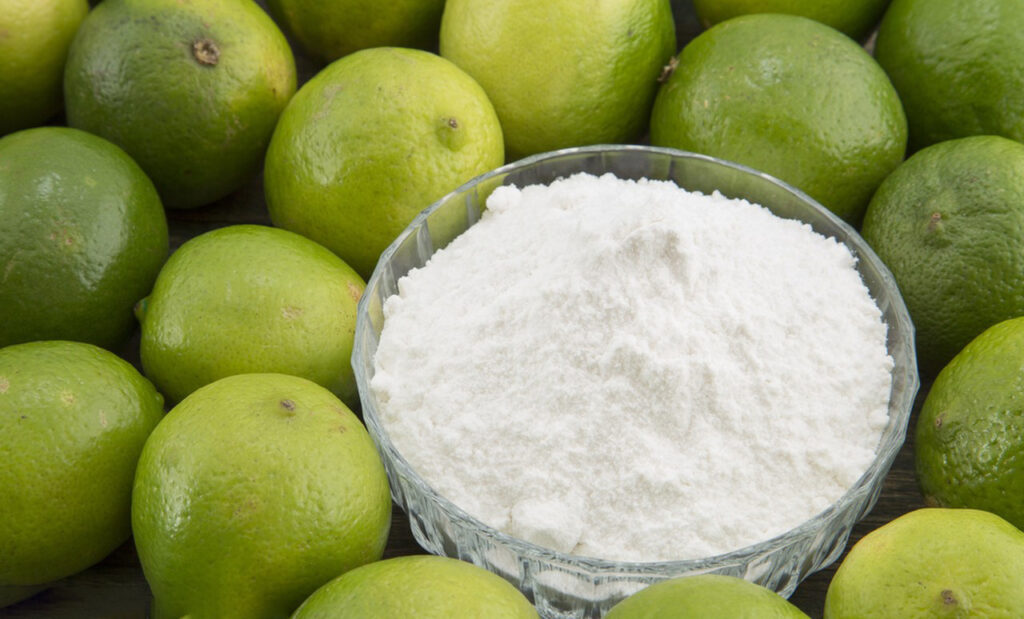


Unlike the alkaline, pure alkali is harmless to the human body, but excessive intake may cause a certain stimulation to the digestive system. Therefore, when using edible alkali, pay attention to use it in appropriate amount to avoid excess.
What is the difference between Caustic Soda (Sodium Hydroxide) and Soda Ash (Sodium Carbonate)?
Ingredients:
Caustic Soda:The main component of the caustic soda is sodium hydroxide, which is a strong alkaline substance.
Soda Ash:The main ingredients of soda ash are sodium carbonate, which is a kind of inorganic salt.


Pureness:
The purity of edible alkali is relatively low, containing a certain impurities; and the purity of the alkali is higher.


Physical Properties:
Caustic Soda: Appears as a white crystalline solid; highly hygroscopic and corrosive.
Soda Ash: Appears as a white powder or granular solid; less corrosive compared to caustic soda.


Safety:
Caustic Soda has strong corrosiveness, and directly contact or error can cause serious damage. It is necessary to strictly observe the obey of strictly. Safety operation regulations.
Soda Ash are harmless to the human body under an appropriate amount, but excessive intake may lead to dysfunction in the body in the body.


Chemical Behavior:
Caustic Soda: Strong alkali with a high pH; reacts vigorously with acids and water, releasing heat.
Soda Ash: Moderate alkali; reacts with acids to produce carbon dioxide gas and water.


Uses:
Caustic Soda is mainly used for industrial production, such as papermaking and chemical industry.
Soda Ash is mainly used for food processing and daily cleaning, such as the production of noodles and cakes.


Different production processes
Caustic soda is a midstream product of the chlor-alkali industry chain. Its production method evolved from the causticizing process to the electrolytic process, and finally to the currention-exchange membrane electrolysis method, which has become the mainstream method in China, accounting for over 99% of production, resulting in relatively uniform production processes.
The production processes of soda ash are divided into the ammonia-soda process, the combined soda process, and the natural soda process. The ammonia-soda process accounts for about 49%, the combined soda process for 46%, and the natural soda process for about 5%.


Product Classification Differences
Soda ash is classified into light and dense types, both in solid form, distinguished by density.
Caustic soda comes in liquid and solid forms:
Liquid Caustic Soda: Based on sodium hydroxide content, available in concentrations of 30%, 32%, 42%, 45%, and 50%, with 32% and 50% being the mainstream specifications.
Solid Caustic Soda: Mainly 99% sodium hydroxide flake caustic soda.
In China, liquid caustic soda production accounts for over 80% of the total, while 99% flake caustic soda accounts for about 14%.


Conclusion
By understanding the differences in the aspects of nature, composition, application, and safety of the above -mentioned caustic soda (sodium hydroxide) and soda ash (sodium carbonate), we must distinguish the dangerous items in life and keep it properly. Industries can select the appropriate chemical for their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and safety in their processes.
For more information on our sodium hydroxide products, visit EAPEARL’s Sodium hydroxide page.








