Butyl Acetate
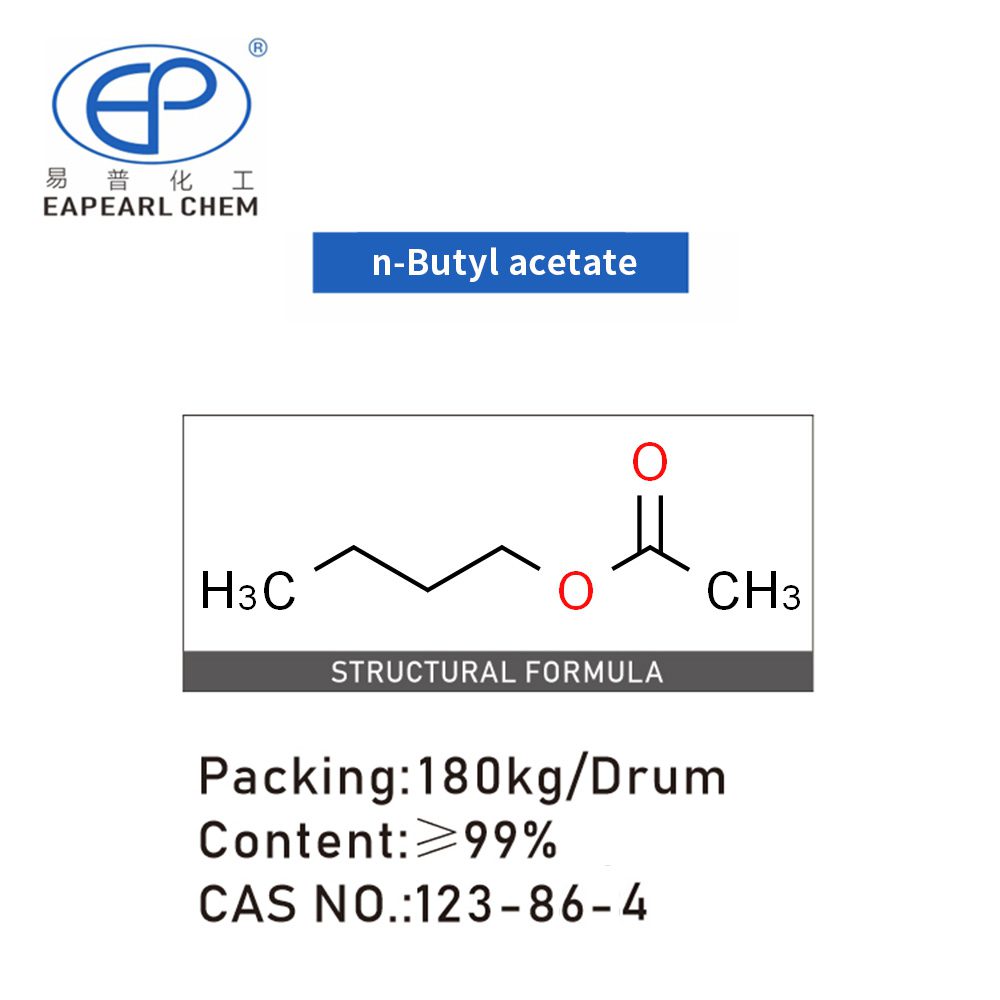

Introduction: Butyl acetate, also known by its systematic name ethyl acetate, is a colorless, flammable liquid primarily used as a solvent in the production of paints and lacquers. With the chemical formula C6H12O2, it is an ester of acetic acid and butanol. Butyl acetate is notable for its sweet smell of banana or apple, making it a popular choice in flavorings and fragrances.
Synonyms: n-Butyl acetate, BTAC, Butyl ethanoate, BUTYLACETAT 85 P, N-BUTYLACETATEESTER, Essigsure-n-butylester, Acetic acid butyl ester, Acetic acid n-butyl ester
Nature: As a solvent, butyl acetate possesses excellent dissolving properties for various substances, making it valuable in numerous industrial applications. It is characterized by its low toxicity and pleasant aroma, which contrasts with the harsh chemical odors of other solvents. Butyl acetate has a boiling point of 126 °C (259 °F) and is less dense than water, with a density of 0.882 g/cm³. It is sparingly soluble in water but mixes well with most organic solvents.
Table of Contents
Butyl Acetate Packaging Information






| Butyl Acetate Packaging | Capacity | 20GP | 40GP |
| drum | 180 kg /drum | total 80 drums, Net 14.4 ton | total 136 drums, Net 24.48 ton |
| IBC drum | 860 kg /IBC | total 20 IBC, Net 17.2 ton | total 30 IBC, Net 25.8 ton |
| ISO Tank | 20.5 ton /ISO Tank | 1 ISO Tank, Net 20.5 ton | N/A |
For butyl acetate, we welcome you to test and check the quality, if you need a sample please contact our sales team to discuss your sample requirements, we believe that our product quality is suitable for the specific application. We provide samples free of charge but the shipping cost will be borne by you.
Applications of Butyl Acetate
Butyl acetate is a versatile solvent with a wide range of applications across various industries due to its excellent solvency properties, fast evaporation rate, and distinct fruity odor. Below are detailed insights into its specific applications:
Paints and Coatings Industry
In the paints and coatings industry, butyl acetate’s role extends beyond simply acting as a solvent. It plays a crucial part in adjusting the paint’s flow and application characteristics, enabling a uniform distribution of paint without brush marks, leading to a flawless finish. Its compatibility with a wide range of resins, including acrylics, vinyls, and alkyds, makes it an indispensable component in varnishes, lacquers, and enamels. This solvent’s ability to dissolve different materials while ensuring a quick drying time contributes to its utility in automotive refinishing, marine paints, and furniture lacquers, where efficiency and aesthetic quality are paramount.




Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
In cosmetics, particularly nail care, butyl acetate is prized not only for its solvent properties but also for its contribution to the product’s overall performance and user experience. By facilitating the smooth application of nail polish, it helps in achieving a glossy, even finish that is resistant to chipping and peeling. Its role in nail polish removers is equally important, where it effectively dissolves the polish, allowing for easy removal without excessive drying or damage to the nail surface. The pleasant aroma of butyl acetate enhances the sensory aspects of cosmetic products, making them more appealing to consumers.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Butyl acetate’s application in the pharmaceutical industry is multifaceted. It not only serves as a solvent in the extraction and purification of drugs but also plays a role in the manufacturing process of medicinal coatings. These coatings are crucial for various reasons, including protecting the active ingredient, masking the taste of bitter medications, and controlling the release of the drug into the body. The solvent’s properties ensure that the coatings are applied uniformly and dry quickly, essential for maintaining the integrity and efficacy of the medication.




Food Flavorings
The use of butyl acetate as a flavoring agent in the food industry capitalizes on its fruity aroma to enhance or introduce flavors in confectioneries, baked goods, and beverages. It is particularly valued for creating artificial apple and banana flavors, adding a natural-tasting sweetness that can enhance the product’s appeal. The solvent’s volatility ensures that the flavor is released promptly upon consumption, providing an immediate burst of taste. Compliance with food safety standards is critical in this application, ensuring that the solvent does not pose any health risks when ingested in trace amounts.
Adhesives and Sealants
Butyl acetate’s role in adhesives and sealants is critical for achieving the desired viscosity and tackiness, ensuring that the adhesive bonds effectively to a variety of surfaces. Its application is widespread, from household glues to industrial-strength adhesives used in construction and automotive industries. The solvent’s rapid evaporation rate is a key feature in spray adhesives, where a quick set-up time is necessary. Additionally, its use in sealants enhances their application properties, ensuring a durable, flexible seal that withstands environmental factors.



Chemical Industry and Synthesis
In the chemical synthesis realm, butyl acetate is employed not just as a solvent but also as a reactant in the production of high-value chemical intermediates. Its role in synthesizing esters, resins, and other organic compounds is pivotal, where its properties can influence reaction rates, yields, and the purity of the final product. The solvent’s ability to dissolve a wide range of compounds makes it an essential component in purification processes, aiding in the extraction and refinement of chemical products.
Printing Inks
Butyl acetate’s application in printing inks highlights its importance in achieving high-quality print results. It allows for the fine dispersion of pigments and resins, ensuring that the ink adheres well to various substrates, including paper, plastics, and metals. This results in vibrant, durable prints that are resistant to smudging and fading. The solvent’s fast drying property is particularly advantageous in high-speed printing processes, where it contributes to reducing smearing and improving production efficiency.


Each of these applications showcases the versatility and importance of butyl acetate as a solvent across various sectors. Its selection for a particular use depends on balancing its solvency, evaporation rate, and sensory attributes with the specific requirements of the application. If you have any questions about butyl acetate applications, please contact our team of experts.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Technical Data of Butyl Acetate
| Name | Butyl Acetate |
| Synonyms | n-Butyl acetate, BTAC, Butyl ethanoate, BUTYLACETAT 85 P, N-BUTYLACETATEESTER, Essigsure-n-butylester, Acetic acid butyl ester, Acetic acid n-butyl ester |
| CAS | 123-86-4 |
| EINECS | 204-658-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C6H12O2 |
| Molar Mass | 116.16 |
| Density | 0.88 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| Melting Point | -78 °C (lit.) |
| Boling Point | 124-126 °C (lit.) |
| Flash Point | 74°F |
| JECFA Number | 127 |
| Water Solubility | 0.7 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Solubility | 5.3g/l |
| Vapor Presure | 15 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| Vapor Density | 4 (vs air) |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Specific Gravity | 0.883 (20/20℃) |
| Color | ≤10(APHA) |
| Odor | Characteristic; agreeable fruity (in low concentrations); non residual. |
| Exposure Limit | TLV-TWA 150 ppm (~710 mg/m3) (ACGIH,MSHA, and OSHA); TLV-STEL 200 ppm(~950 mg/m3); IDLH 10,000 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Maximum wavelength(λmax) | [‘λ: 254 nm Amax: 1.0’, |
| , ‘λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.20’, | |
| , ‘λ: 275 nm Amax: 0.04’, | |
| , ‘λ: 300 | |
| Merck | 141,535 |
| BRN | 1741921 |
| PH | 6.2 (5.3g/l, H2O, 20℃)(External MSDS) |
| Storage Condition | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| Stability | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, strong bases. |
| Explosive Limit | 1.4-7.5%(V) |
| Refractive Index | n20/D 1.394(lit.) |
| Physical and Chemical Properties | Colorless flammable liquid with pleasant fruit aroma. |
| boiling point 126 ℃ | |
| freezing point -77.9 ℃ | |
| relative density 0.8825 | |
| refractive index 1.3951 | |
| flash point 33 ℃ | |
| solubility, an organic solvent such as an ether is miscible, and is less soluble in water than a lower homolog. | |
| colorless liquid with fruit aroma. Relative density (20 ℃/4 ℃)0.8825, freezing point -73.5 ℃, boiling point 126.11 ℃, Flash Point (opening) 33 ℃, ignition point 421 ℃, refractive index 1. 3941, specific heat capacity (20 deg C) 1. 91KJ/(kg, K), viscosity (20 degrees C) 0.734mPas, solubility parameter delta = 8.5. Soluble in alcohol, ketone, ether and other organic solvents, slightly soluble in water. In case of high heat, open flame, oxidant has caused the risk of combustion. The vapor forms an explosive mixture with air with an explosion limit of 1.4%-8.0%(vol). Low toxicity, anesthesia and irritation, the highest allowable concentration in the air 300mg/m3(or 0.015%). | |
| HS Code | 2915 33 00 |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 14.13 g/kg (Smyth) |
| LogP | 1.82-2.3 at 25℃ |
| Dielectric constant | 5.0(20℃) |
Butyl Acetate Production
The production of butyl acetate typically involves the esterification reaction of acetic acid with butanol. This process can be catalyzed by an acid, such as sulfuric acid, under controlled conditions. The production process can be broken down into several key steps, each crucial for the efficient synthesis and purification of butyl acetate. The following is a detailed description of the production process:
1. Raw Material Preparation
- Acetic Acid: A carboxylic acid that acts as one of the reactants.
- Butanol: An alcohol that can be n-butanol, isobutanol, sec-butanol, or tert-butanol, depending on the desired butyl acetate isomer.
- Acid Catalyst: Typically sulfuric acid, used to accelerate the esterification reaction.
2. Esterification Reaction
- The esterification process is initiated by mixing acetic acid with butanol in a reaction vessel. The acid catalyst is then added to the mixture.
- The reaction mixture is heated to a temperature range of 120°C to 140°C to facilitate the reaction.
- Under these conditions, acetic acid and butanol react according to the following equation: CH3COOH+C4H9OH→CH3COOC4H9+H2O
- This reaction is reversible, and the equilibrium can be shifted towards the product side by continuously removing the water formed during the reaction, typically by using a water separator or by applying vacuum to the system to evaporate the water.
3. Product Recovery
- After the esterification reaction, the mixture contains butyl acetate, unreacted acetic acid, butanol, water, and the acid catalyst.
- The mixture is first subjected to a distillation process to separate the butyl acetate from the heavier components like the acid catalyst and the lighter components such as water and unreacted reactants.
- Butyl acetate is collected as a distillate at its boiling point of approximately 126°C.
4. Purification
- The distilled butyl acetate may still contain traces of acetic acid, butanol, and water, which can affect its purity and performance.
- A further purification step, such as a second distillation or washing with a base to neutralize any residual acid, may be required to achieve high-purity butyl acetate.
- The final product is then tested for purity and quality before being packaged and stored.
5. Waste Management and Recycling
- The production process generates waste, including water containing traces of acetic acid and butanol, as well as acid catalyst residues.
- Waste streams are treated according to environmental regulations, with efforts made to recycle and recover materials wherever possible. For example, unreacted acetic acid and butanol can be recovered and reused in the esterification process.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
How can we handle your order?


step 1
We will communicate with you within 24 hours after you send an enquiry.


step 2
If you need sample testing, we will send samples within 5 days,≤50kg, Express delivery recommended, usually called as DDU service; delivery time 5-7 days. Door to door service.


step 3
If you need bulk goods after the sample test is qualified, we will ship the goods to the port and keep the samples within 6 days after the order is confirmed. Sea shipping recommended, usually called as FOB, CFR, or CIF service.delivery time 10-45 days. Port to port service.


step 4
After waiting for you to receive the goods, we will arrange professional staff to pay a return visit within 7 days.
Difference Between Ethyl Acetate and Butyl Acetate
Ethyl acetate and butyl acetate are clear liquids with a fruity odors. In cosmetics and personal care products, ethyl acetate and butyl acetate are used in the formulation of nail polish, nail polish removers, basecoats, and other manicuring products. The difference between ethyl acetate and butyl acetate primarily lies in their molecular structure and the length of their carbon chains, which subsequently affects their physical and chemical properties. Here’s a concise explanation:
Chemical Structure and Formula
- Ethyl Acetate: Has the chemical formula C4H8O2, composed of an ethyl group (C2H5) linked to an acetate group.
- Butyl Acetate: Has the chemical formula C6H12O2, consisting of a butyl group (C4H9) attached to an acetate group.
Molecular Weight
- Ethyl Acetate: Lighter, with a molecular weight of about 88.11 g/mol.
- Butyl Acetate: Heavier, with a molecular weight of about 116.16 g/mol.
Boiling Point
- Ethyl Acetate: Boils at a lower temperature, around 77°C (171°F), indicating less intermolecular force.
- Butyl Acetate: Has a higher boiling point of approximately 126°C (259°F), due to stronger van der Waals forces from the longer carbon chain.
Solubility in Water
- Ethyl Acetate: Moderately soluble in water.
- Butyl Acetate: Slightly soluble, with solubility decreasing as the alkyl chain length increases.
Odor
- Both have a sweet, fruity odor, but:
- Ethyl Acetate is often described as having a solvent-like smell.
- Butyl Acetate tends to have a more distinct banana-like or fruity odor.
Usage and Applications
- Ethyl Acetate is commonly used as a solvent in paints, coatings, adhesives, printing inks, and nail polish removers.
- Butyl Acetate is used in the manufacture of lacquers and paints, as a solvent in the production of plastics and synthetic fibers, and as a fragrance ingredient in perfumes and foods due to its pleasant smell and less volatile nature.
Environmental Impact
- Both compounds are considered to be rapidly biodegradable. However, ethyl acetate may contribute more to photochemical smog due to its higher volatility, compared to butyl acetate.
Volatility
- Ethyl Acetate is more volatile because of its lower boiling point.
- Butyl Acetate is less volatile, making it suitable for applications where a slower evaporation rate is desirable.
In essence, the main differences between ethyl acetate and butyl acetate lie in their molecular structures and the length of their carbon chains, which influence their physical properties and suitability for various applications. Ethyl acetate’s lower molecular weight and boiling point make it more volatile and suitable for uses requiring fast evaporation, while butyl acetate’s longer carbon chain lends to applications benefiting from its less volatile nature and pleasant odor.
Butyl Acetate Storage and Environmental Disposal
Butyl acetate, a colorless, flammable liquid with a fruity odor, is widely used in various industrial and commercial applications, including the manufacturing of paints, coatings, adhesives, and cosmetics. Proper storage and disposal of butyl acetate are crucial due to its chemical properties and potential environmental impact. This part provides guidelines on the storage and environmental disposal of butyl acetate, emphasizing safety practices and regulatory compliance.
Storage
Conditions
Butyl acetate should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and sources of ignition. Storage containers must be tightly sealed to prevent evaporation and leakage, as butyl acetate’s volatile organic compounds (VOCs) contribute to air pollution and may pose health risks upon inhalation. Materials used in the construction of storage containers and facilities should be resistant to butyl acetate to prevent chemical corrosion.
Safety Measures
Fire prevention is a critical aspect of storing butyl acetate due to its flammability. Storage areas should be equipped with appropriate fire-fighting measures, including extinguishers and sprinkler systems. Spill containment measures must be in place to manage accidental leaks or spills, preventing soil and water contamination. Personnel handling butyl acetate storage should be trained in proper safety procedures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Environmental Disposal
Regulations
Disposal of butyl acetate must comply with local, national, and international environmental regulations. These regulations typically require that hazardous chemicals like butyl acetate be treated or neutralized before disposal to minimize their impact on the environment. Disposal records should be maintained as part of regulatory compliance.
Methods
Butyl acetate should not be disposed of in regular trash or poured down drains, as it can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic life. Instead, it should be collected and sent to facilities equipped to handle hazardous waste disposal. These facilities may employ methods such as incineration in specially designed incinerators that capture and treat emissions or chemical neutralization to render the waste non-hazardous.
Health and Environmental Impact
Butyl acetate can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system upon exposure. Its volatility contributes to VOC emissions, which play a significant role in the formation of ground-level ozone and smog, posing risks to human health and the environment. Proper storage and disposal practices are essential to mitigate these risks.
Regulatory Considerations
Regulatory frameworks governing the storage and disposal of butyl acetate include the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) in the United States, the European Waste Catalogue (EWC) in the European Union, and other region-specific guidelines. These regulations ensure that hazardous materials are managed in a manner that protects public health and the environment.
Advantages of the Chinese Butyl Acetate Market
The Chinese butyl acetate market has experienced significant growth and development over the past few decades, emerging as a leading player in the global chemical industry. Butyl acetate, a solvent known for its wide range of applications in industries such as paints and coatings, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food flavorings, has seen increasing demand both domestically and internationally. This part explores the advantages of the Chinese butyl acetate market, highlighting the factors that contribute to its prominence.
Strategic Industry Positioning
China’s strategic positioning as a global manufacturing hub has significantly benefited the butyl acetate market. The country’s vast industrial sector, encompassing everything from automotive to electronics and textiles, provides a substantial internal market for butyl acetate. This internal demand stabilizes the market and fuels continuous investment in production capacities and technological advancements.
Cost-Competitive Manufacturing
One of the key advantages of the Chinese butyl acetate market is its cost-competitive manufacturing environment. Leveraging economies of scale, efficient production processes, and lower labor costs, Chinese manufacturers can offer butyl acetate at competitive prices. This pricing advantage makes Chinese butyl acetate attractive to international buyers, enhancing its export potential.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
Chinese chemical manufacturers have made significant strides in technological advancements and innovation in butyl acetate production. Investments in research and development have led to more efficient production methods, reducing waste and lowering production costs. These advancements also include the development of greener, more environmentally friendly production processes, appealing to markets with strict environmental regulations.
Robust Supply Chain and Logistics
China boasts a well-developed and efficient logistics infrastructure, including a vast network of ports, railways, and roads. This robust logistics system ensures the smooth export and import of raw materials and finished products, contributing to the market’s efficiency and responsiveness. The ability to quickly and reliably supply butyl acetate to both domestic and international markets is a significant advantage for Chinese producers.
Government Support and Regulatory Environment
The Chinese government has historically supported the chemical industry through favorable policies, including subsidies, tax incentives, and investment in infrastructure. This supportive regulatory environment has encouraged growth and investment in the butyl acetate market, helping to establish China as a key player in the global chemical industry.
Growing International Presence
Chinese butyl acetate manufacturers have increasingly looked beyond domestic markets, expanding their presence internationally through exports and strategic partnerships. By establishing a strong foothold in key global markets, Chinese producers are not only capitalizing on international demand but also enhancing their global competitiveness and brand recognition.
Our Team
FAQs of Butyl Acetate
A1: Butyl acetate is an organic compound used widely as a solvent in the production of paints, coatings, adhesives, and cosmetics. Known for its sweet, fruity smell, it is a preferred choice in industries that require a high-quality solvent for their products.
A2: For Businesses:
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Registration: Demonstrates compliance with environmental safety standards.
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) Compliance: Shows adherence to workplace safety regulations.
- Local Fire Department Permits: For storage and handling of flammable substances.
For Individuals:
- Generally, individuals are not encouraged to purchase butyl acetate due to its hazardous nature unless they possess appropriate safety certifications and have a legitimate use that complies with local regulations.
A3: Butyl acetate should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area away from heat sources and open flames. Use containers made of materials compatible with butyl acetate, and ensure they are tightly sealed to prevent leaks and minimize evaporation.
A4: Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, including gloves, goggles, and respirators.
Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in the area where butyl acetate is used to avoid inhalation hazards.
Spill Management: Have spill containment and cleanup procedures in place.
A5: Yes, butyl acetate is classified as a flammable liquid with potential health risks if inhaled, ingested, or comes into contact with skin. It can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system.
A6: Yes, butyl acetate is biodegradable. It undergoes degradation by microorganisms in the environment, breaking down into simpler, non-toxic substances over time. This property makes it less harmful to ecosystems compared to many other organic solvents.
A7: Absolutely. We offer 100g-200g samples, with the client only covering shipping costs.
A8: Standard lead times are approximately 2-4 weeks, varying based on order size and destination.
A9: Our standard payment terms include a 30% advance and the balance against delivery, but terms can be negotiated for long-term partnerships.
A10: Yes, we offer comprehensive after-sales support, addressing any post-purchase queries or concerns.
A11: As a supplier, in order to provide you with an accurate quote for your product, please inform us of the quantity you require, the required purity specifications, any specific packaging needs, your shipping location, and whether your application requires any customization requirements or certifications.


