Diethyl carbonate
Welcome to the world of Diethyl Carbonate (DEC), where sustainability meets versatility. Discover how DEC can revolutionize your industry with its eco-friendly properties and diverse applications.

Introduction:
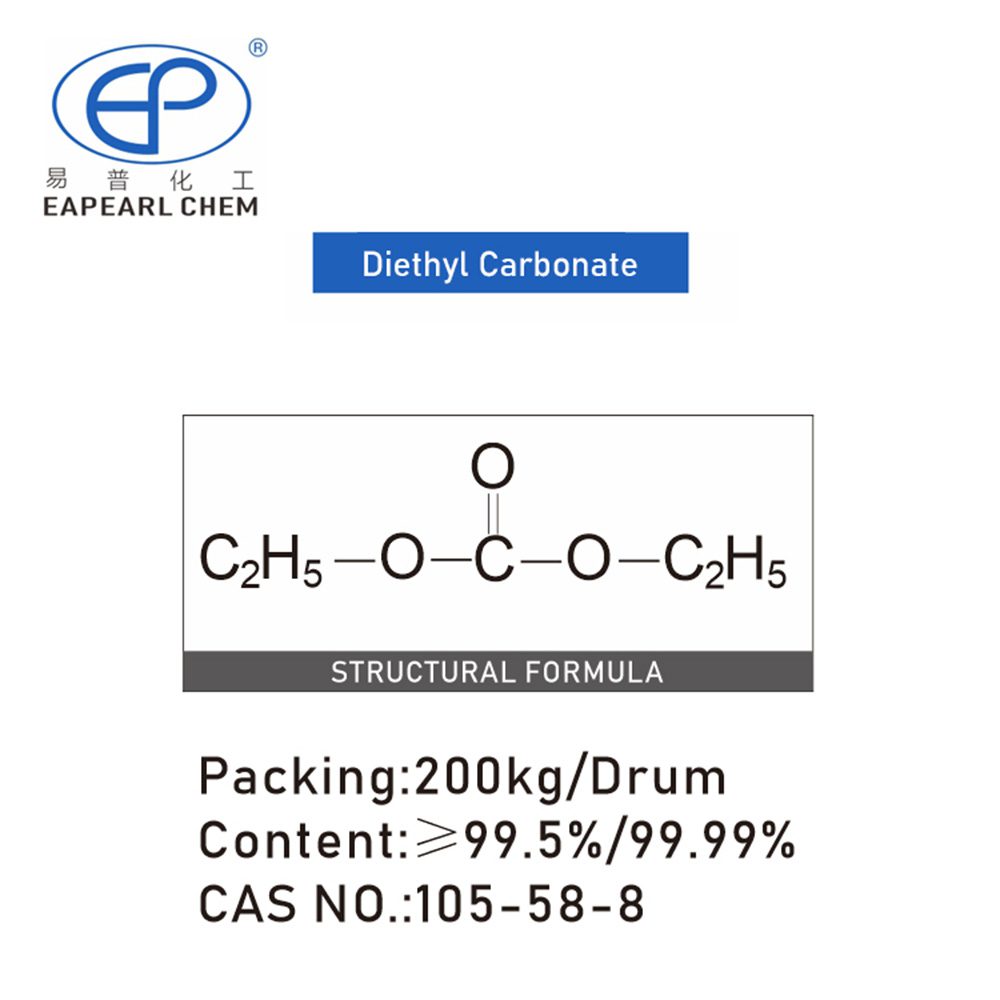
Diethyl carbonate, also known by its chemical formula (C5H10O3), is an organic compound belonging to the ester class. This colorless, flammable liquid boasts a distinctive fruity odor and finds wide utility across industrial sectors due to its versatile properties.
synonyms:
DEC, DPD1, TGFB, Ethyl carbonate, Diethyl carbote, Diethyl carbonate, diethyl dicarbonate, Carbonic acid diethyl ester;
Nature:
At ambient conditions, Diethyl Carbonate manifests as a clear liquid with a molecular weight of approximately 118.08 g/mol. Its chemical structure comprises two ethyl groups attached to a carbonate functional group, rendering it a valuable building block in organic synthesis.
Table of Contents
Diethyl Carbonate Packaging Information
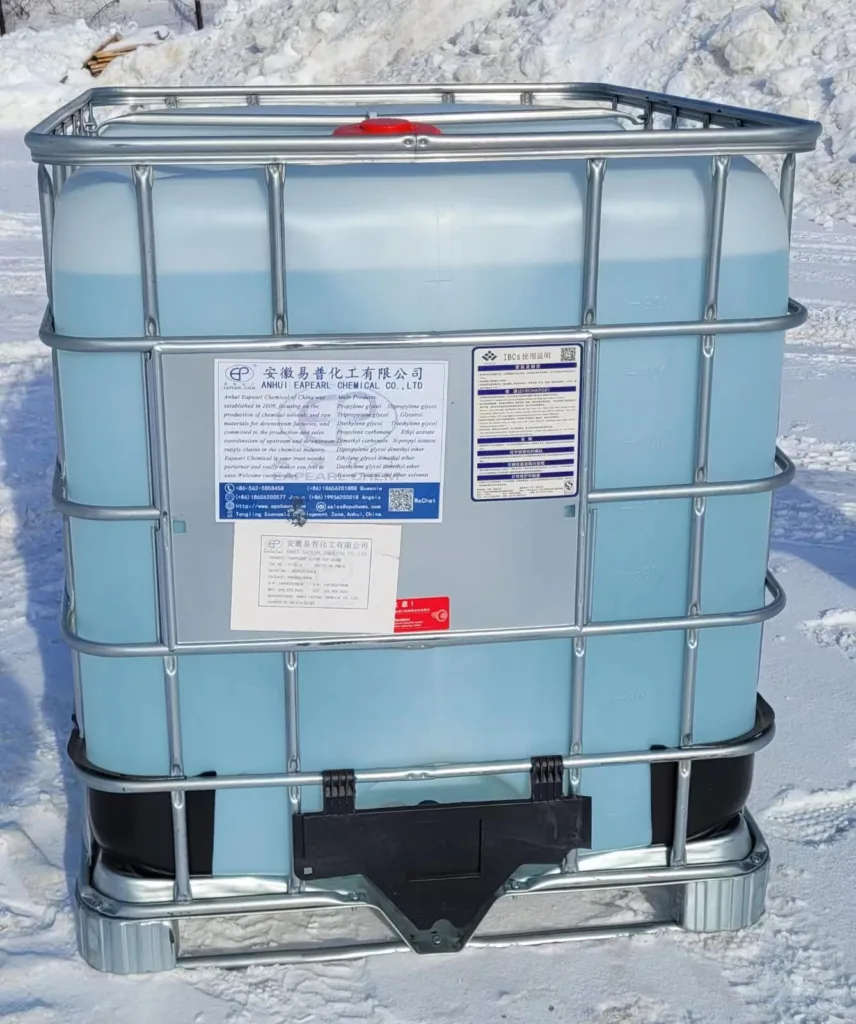






| DEC packaging | Capacity | 20GP | 40GP |
| drum | 200 kg /drum | total 80 drums, Net 16 ton | total 128 drums, Net 25.6 ton |
| IBC drum | 800 kg /IBC | total 20 IBC, Net 16 ton | total 32 IBC, Net 25.6 ton |
| ISO Tank | 18.5 ton /ISO Tank | 1 ISO Tank, Net 18.5 ton | N/A |
For diethyl carbonate, we welcome you to test and check the quality, if you need a sample please contact our sales team to discuss your sample requirements, we believe that our product quality is suitable for the specific application. We provide samples free of charge but the shipping cost will be borne by you.
Applications of Diethyl Carbonate
Diethyl carbonate is an aprotic, environment-friendly organic solvent, which is commonly used as a solvent for cellulose ethers, nitrocellulose, natural and synthetic resins. In the electronic industry, it is usually used as an electrolyte solvent for lithium-ion batteries and capacitors. Its electrochemical stability is good. It can improve the electrolyte’s low temperature performance.
Application in Lithium-Ion Battery Manufacturing:
Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) is a crucial component in the production of lithium-ion batteries, which are widely utilized in electronic devices, electric vehicles, and renewable energy storage systems. In battery manufacturing, DEC serves as a solvent for formulating the electrolyte solution, which is essential for facilitating ion transport between the battery’s electrodes during charge and discharge cycles.

Key Aspects of DEC’s Application in Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- Solvent Properties: DEC’s high solvency and compatibility with lithium salts, such as lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6), make it an ideal solvent for formulating the electrolyte solution in lithium-ion batteries. It effectively dissolves lithium salts and other electrolyte additives, ensuring the homogeneity of the electrolyte mixture.
- Improved Electrolyte Performance: The use of DEC in electrolyte formulations contributes to enhanced battery performance, including improved cycling stability, higher energy density, and better safety characteristics. DEC-based electrolytes exhibit favorable properties such as high conductivity, low viscosity, and wide electrochemical stability windows, which are critical for maximizing battery efficiency and reliability.
- Safety and Environmental Considerations: Compared to traditional carbonate-based solvents like ethylene carbonate (EC) or propylene carbonate (PC), DEC offers advantages in terms of safety and environmental impact. It has lower volatility and reduced flammability, which enhances safety during battery manufacturing and usage. Additionally, DEC’s relatively low toxicity and biodegradability align with efforts to promote environmentally sustainable battery technologies.

Application as a Solvent in Pharmaceutical Synthesis:
Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) serves as a versatile solvent and intermediate in pharmaceutical synthesis, contributing to the production of a wide range of pharmaceutical compounds, drug formulations, and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Its unique chemical properties make it an attractive option for various synthetic transformations and processes in pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Key Aspects of DEC’s Application in Pharmaceutical Synthesis:
- Versatile Solvent: DEC serves as a versatile reaction medium for various organic transformations, including esterifications, transesterifications, and carbonylation reactions. Its ability to dissolve both polar and non-polar organic compounds makes it suitable for a wide range of synthetic applications in pharmaceutical chemistry.
- Selective Reactivity: DEC’s chemical reactivity and selectivity enable specific transformations of functional groups, facilitating the synthesis of complex molecules and pharmaceutical intermediates. It participates in reactions such as acylation, alkylation, and nucleophilic substitution, allowing for precise control over reaction pathways and product formation.
- Green Chemistry Benefits: DEC is recognized as a greener solvent option compared to traditional solvents used in pharmaceutical synthesis, such as chlorinated solvents or aromatic hydrocarbons. Its relatively low toxicity, biodegradability, and favorable environmental profile align with the principles of green chemistry, promoting sustainable manufacturing practices and minimizing environmental impact.
Application as an Additive in Coatings and Paints:
Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) serves as a valuable additive and solvent in the formulation of coatings and paints, contributing to the enhancement of product performance, aesthetics, and environmental sustainability. Its unique properties make it an attractive choice for various coating applications, including architectural coatings, automotive paints, and industrial coatings.


Key Aspects of DEC’s Application as an Additive in Coatings and Paints:
- Solvent and Diluent: DEC functions as a solvent and diluent in coatings and paints formulations, aiding in the dispersion of pigments, resins, and additives. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of coating components ensures the homogeneity and stability of coating formulations, promoting uniform film formation and surface coverage.
- Viscosity Control: DEC’s solvency properties allow for precise control over the viscosity of coatings and paints formulations. By adjusting the concentration of DEC, formulators can tailor the rheological properties of coatings to meet specific application requirements, such as sprayability, flow, and leveling. DEC-based formulations exhibit optimal viscosity characteristics, enabling ease of application and uniform coating thickness.
- Film Formation and Performance: DEC contributes to the formation of durable and high-performance coating films by promoting the evaporation of volatile components and enhancing the coalescence of resin particles. The incorporation of DEC in coatings formulations results in smooth, defect-free coating surfaces with excellent adhesion, flexibility, and resistance properties, ensuring long-lasting protection and aesthetic appeal.
- Environmental Sustainability: DEC’s relatively low toxicity, biodegradability, and favorable environmental profile make it a preferred additive for environmentally friendly coatings and paints formulations. Its use in eco-friendly coatings aligns with sustainability initiatives and regulatory requirements, supporting efforts to reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions and minimize environmental impact.
Diethyl carbonate is also used in many other fields, including but not limited to: used as a sealing fixative, especially in the fields of electronic components, liquid crystal products, plastic additives, resin curing agents, etc. As chemical analysis reagents and reaction carriers. Used to prepare organic matter extractants such as solvent extractants and extraction agents. If you have any questions about the application of diethyl carbonate, please contact us and our team of experts will give you professional advice.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Technical of Diethyl Carbonate
| Name | Diethyl carbonate |
| Synonyms | DEC, DPD1, TGFB, Ethyl carbonate, Diethyl carbote, Diethyl carbonate, diethyl dicarbonate, Carbonic acid diethyl ester; |
| CAS | 105-58-8 |
| EINECS | 203-311-1 |
| Molecular Formula | C5H10O3 |
| Molar Mass | 118.13 |
| Density | 0.975 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| Melting Point | -43 °C (lit.) |
| Boling Point | 126-128 °C (lit.) |
| Flash Point | 88°F |
| Water Solubility | Negligible |
| Solubility | 18.8mg/l insoluble |
| Vapor Presure | 10 mm Hg ( 23.8 °C) |
| Vapor Density | 4.1 (vs air) |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Color | Clear |
| Odor | Pleasant, etheral; mild and nonresidual. |
| Merck | 143,780 |
| BRN | 956591 |
| PH | 6.3 (1g/l, H2O) |
| LogP | 1.21 at 25℃ |
| Storage Condition | no restrictions. |
| Stability | Stable. Flammable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong bases, reducing agents, oxidizing agents. Protect from moisture. |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Explosive Limit | 1.4-11.0%(V) |
| Refractive Index | n20/D 1.384(lit.) |
| Physical and Chemical Properties | Colorless transparent liquid, slightly irritating odor. |
| melting point -43 ℃ | |
| boiling point 126.8 ℃ | |
| relative density 0.975 | |
| refractive index 1.3846 | |
| flash point 32.8 ℃ | |
| solubility insoluble in water, soluble in alcohol, ether and other organic solvents. | |
| HS Code | 2920 90 10 |
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: > 4900 mg/kgLC50 (inhalation) > 21 mg/kg (mouse)TDL0 500 mg/kg (mouse)LD50 (s.c.) 8500 mg/kg (rat) |
Diethyl Carbonate Production
The production of Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) involves several methods, including transesterification, phosgenation, and carbonylation. Below is an outline of the specific production processes for Diethyl Carbonate:
Transesterification Method:
Reactants: The transesterification process typically involves the reaction of ethylene carbonate (EC) with ethanol (EtOH) in the presence of a catalyst.
Reaction Conditions: The reaction is typically carried out under reflux conditions with the addition of a suitable catalyst, such as alkali metal alkoxides or acidic catalysts like p-toluenesulfonic acid.
Transesterification Reaction: Ethylene carbonate (EC) reacts with ethanol (EtOH) to form Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) and ethylene glycol (EG) as a byproduct: EC + 2EtOH → DEC + EG
Separation and Purification: After the reaction, the mixture is typically distilled to separate Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) from unreacted ethanol and ethylene glycol. Further purification steps, such as distillation or molecular sieves, may be employed to obtain high-purity Diethyl Carbonate.
Phosgenation Method:
Reactants: The phosgenation process involves the reaction of ethanol (EtOH) with phosgene (COCl2) in the presence of a suitable solvent and catalyst.
Reaction Conditions: The reaction is typically carried out under controlled conditions, often in the presence of a solvent such as toluene or chloroform and a catalyst such as pyridine or quaternary ammonium salts.
Phosgenation Reaction: Ethanol (EtOH) reacts with phosgene (COCl2) to form Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) and hydrogen chloride (HCl) as a byproduct: COCl2 + 2EtOH → DEC + 2HCl
Separation and Purification: After the reaction, the mixture is typically subjected to distillation to separate Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) from unreacted ethanol and hydrogen chloride. Additional purification steps, such as washing with water or treatment with alkalis, may be employed to remove impurities and obtain high-purity Diethyl Carbonate.
Carbonylation Method:
Reactants: The carbonylation process involves the reaction of ethanol (EtOH) with carbon monoxide (CO) in the presence of a suitable catalyst and promoter.
Reaction Conditions: The reaction is typically carried out under elevated pressure and temperature conditions, often in the presence of a catalyst such as transition metal complexes (e.g., palladium or rhodium) and a promoter such as alkali metal iodides.
Carbonylation Reaction: Ethanol (EtOH) reacts with carbon monoxide (CO) to form Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) and water (H2O) as a byproduct: CO + 2EtOH → DEC + H2O
Separation and Purification: After the reaction, the mixture is typically subjected to distillation or other separation techniques to isolate Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) from unreacted ethanol and water. Additional purification steps, such as fractional distillation or molecular sieves, may be employed to obtain high-purity Diethyl Carbonate.
A comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of these three methods for synthesizing diethyl carbonate is as follows:
| Synthesis Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Transesterification | Environmentally Friendly | Slow Reaction Rate |
| Mild Reaction Conditions | Catalyst Sensitivity | |
| Phosgenation | Versatility | Yield Variability |
| High Purity | Safety Concerns | |
| Efficient Conversion | Environmental Impact | |
| Carbonylation | Scalability | Costly and Complex |
| High Conversion | High Pressure and Temperature | |
| Selectivity | Catalyst Dependency | |
| Catalyst Efficiency | Environmental Concerns |
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
The Dangers of Diethyl Carbonate
Diethyl carbonate is a chemical compound that, like many chemicals, can pose various hazards if not handled properly. It’s essential to be aware of these potential dangers when working with or around DEC. Here are some of the primary hazards associated with diethyl carbonate:
Flammability: Diethyl carbonate is flammable and can form flammable vapor-air mixtures. It has a relatively low flash point, which means it can ignite easily when exposed to an open flame, sparks, or heat sources. Proper storage away from ignition sources is crucial to mitigate this hazard.
Irritation and Toxicity: DEC can be irritating to the skin, eyes, and respiratory system. Prolonged or repeated exposure to DEC vapors or contact with the skin can lead to irritation, redness, and dermatitis. Inhaling DEC vapors may cause respiratory discomfort and lung irritation.
Health Effects: Direct exposure to DEC, especially in high concentrations or without proper personal protective equipment (PPE), can lead to health effects such as headaches, dizziness, nausea, and vomiting. In severe cases or with prolonged exposure, it may affect the central nervous system.
Environmental Impact: Improper disposal of DEC or its release into the environment can have negative ecological consequences. DEC is biodegradable, but it can still harm aquatic life and soil organisms if released in large quantities. Spills should be promptly contained and reported to appropriate authorities.
Chemical Incompatibilities: DEC should not be mixed with incompatible chemicals, as it can react violently. It is important to store DEC away from strong acids, bases, oxidizing agents, and reactive metals to prevent potential chemical reactions.
Storage and Handling Risks: DEC is sensitive to temperature, so it should be stored in a cool, dry place away from heat sources, direct sunlight, and open flames. Handling DEC requires appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety goggles, and adequate ventilation in work areas to minimize exposure to vapors.
Regulatory Compliance: Users and handlers of DEC must adhere to local, regional, and national regulations governing the safe handling, storage, transportation, and disposal of hazardous chemicals. Compliance with these regulations is essential to ensure safety and environmental protection.
It is crucial to exercise caution and follow safety guidelines, including the use of appropriate safety equipment and adherence to established protocols when working with Diethyl Carbonate. Prior to using DEC in any industrial or laboratory setting, individuals should receive proper training on its safe handling, storage, and disposal to minimize risks and ensure the well-being of personnel and the environment.
Diethyl Carbonate Storage
Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) is a chemical compound widely used in various industrial applications, including lithium-ion battery manufacturing, pharmaceutical synthesis, and coatings formulations. Proper storage and disposal of Diethyl Carbonate are essential to ensure safety, environmental protection, and regulatory compliance.
Storage:
Diethyl Carbonate should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat, direct sunlight, and sources of ignition. It should be kept in tightly sealed containers made of compatible materials, such as stainless steel, glass, or high-density polyethylene (HDPE), to prevent leakage or evaporation.
Key Considerations for Diethyl Carbonate Storage:
- Temperature Control: Maintain storage temperatures below the compound’s flash point to minimize the risk of fire or explosion.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in storage areas to prevent the accumulation of vapors and reduce the risk of exposure to hazardous concentrations.
- Segregation: Store Diethyl Carbonate away from incompatible substances, such as strong acids, bases, oxidizing agents, and reactive metals, to prevent potential chemical reactions or contamination.
- Labeling: Clearly label containers with the chemical name, hazard symbols, safety precautions, and emergency contact information to facilitate safe handling and identification.
Advantages of the Chinese Diethyl Carbonate Market
The Chinese Diethyl Carbonate (DEC) market has witnessed significant growth and prominence in recent years, driven by a combination of factors such as expanding industrial applications, technological advancements, and favorable regulatory policies. This page aims to explore the advantages and opportunities presented by the Chinese DEC market, shedding light on its key strengths and competitive advantages.
Growing Demand and Market Potential: The Chinese DEC market is experiencing robust demand fueled by the expanding electronics, pharmaceutical, and coatings industries. With the increasing adoption of lithium-ion batteries in electric vehicles (EVs) and renewable energy storage systems, the demand for DEC as a solvent in battery electrolytes is expected to surge. Moreover, the pharmaceutical sector’s reliance on DEC as an intermediate in drug synthesis and coatings industry’s utilization of DEC as an additive further contribute to market growth.
Strategic Positioning and Infrastructure: China’s strategic positioning as a manufacturing hub and its well-established chemical industry infrastructure provide a competitive edge in the DEC market. The country’s extensive network of chemical manufacturers, research institutions, and logistical capabilities enables efficient production, distribution, and export of DEC and related products. Additionally, China’s abundant availability of raw materials and skilled workforce support the sustainable growth of the DEC market.
Technological Innovation and Research Advancements: Continuous technological innovation and research advancements in the Chinese chemical industry drive product development and process optimization in DEC production. Collaborative efforts between academia, industry players, and government initiatives foster innovation in DEC synthesis methods, leading to enhanced efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and environmental sustainability. These advancements position China at the forefront of DEC production technology, fostering competitiveness in the global market.
Regulatory Support and Policy Initiatives: China’s supportive regulatory environment and policy initiatives play a pivotal role in facilitating market growth and investment in the DEC sector. Government policies aimed at promoting sustainable development, innovation, and industrial upgrading incentivize investment in DEC production facilities and research projects. Moreover, regulatory frameworks ensuring product quality, safety, and environmental compliance bolster consumer confidence and market stability.
Global Market Integration and Export Opportunities: The Chinese DEC market benefits from its integration into the global supply chain and export-oriented manufacturing capabilities. China’s extensive trade networks and partnerships enable access to international markets, creating export opportunities for DEC and related products. The country’s competitive pricing, quality standards, and reliability contribute to its attractiveness as a preferred supplier of DEC on the global stage.
Our Team
FAQs of Diethyl Carbonate
A1: Diethyl Carbonate is utilized as a solvent, intermediate, and additive in numerous industrial processes. It serves as a key component in lithium-ion battery electrolytes, pharmaceutical synthesis reactions, coatings and paints formulations, and as a solvent for extracting natural products.
A2: When handling Diethyl Carbonate, it is essential to observe proper safety precautions. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats. Additionally, ensure adequate ventilation in the work area to minimize exposure to vapors. Store DEC in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat, sparks, and open flames. Familiarize yourself with the material safety data sheet (MSDS) for DEC and follow recommended handling procedures.
A3: Yes, to purchase Diethyl Carbonate, it is necessary to confirm the qualification of purchasing and handling dangerous chemicals. Customers must demonstrate compliance with relevant regulations and possess the appropriate qualifications for handling hazardous chemicals. This typically involves obtaining the necessary permits, licenses, or certifications from regulatory authorities, such as environmental protection agencies or occupational safety agencies.
A4: Qualification for purchasing and handling Diethyl Carbonate involves completing training programs on chemical safety, hazardous material handling, and regulatory compliance. Additionally, individuals or organizations may need to undergo inspections, assessments, or audits to ensure compliance with safety and environmental standards. Contact your local regulatory agency or chemical supplier for guidance on obtaining the required qualifications.
A5: When using Diethyl Carbonate, it is important to adhere to environmental regulations governing the storage, transportation, and disposal of hazardous chemicals. Ensure compliance with local, regional, and national environmental regulations to minimize environmental impact and prevent pollution. Implement proper waste management practices and disposal methods in accordance with regulatory requirements.
A6: Yes, Diethyl Carbonate can be recycled or reused in certain applications, depending on its purity and condition. Recycling processes may involve distillation, filtration, or chemical treatment to recover DEC from waste streams or byproducts. Reusing DEC in compatible processes or formulations can help minimize waste generation and promote resource efficiency.
A7: Absolutely. We offer 100g-200g samples, with the client only covering shipping costs.
A8: Standard lead times are approximately 2-4 weeks, varying based on order size and destination.
A9: Our standard payment terms include a 30% advance and the balance against delivery, but terms can be negotiated for long-term partnerships.
A10: Yes, we offer comprehensive after-sales support, addressing any post-purchase queries or concerns.
A11: As a supplier, in order to provide you with an accurate quote for your product, please inform us of the quantity you require, the required purity specifications, any specific packaging needs, your shipping location, and whether your application requires any customization requirements or certifications.


