Dimethyl carbonate
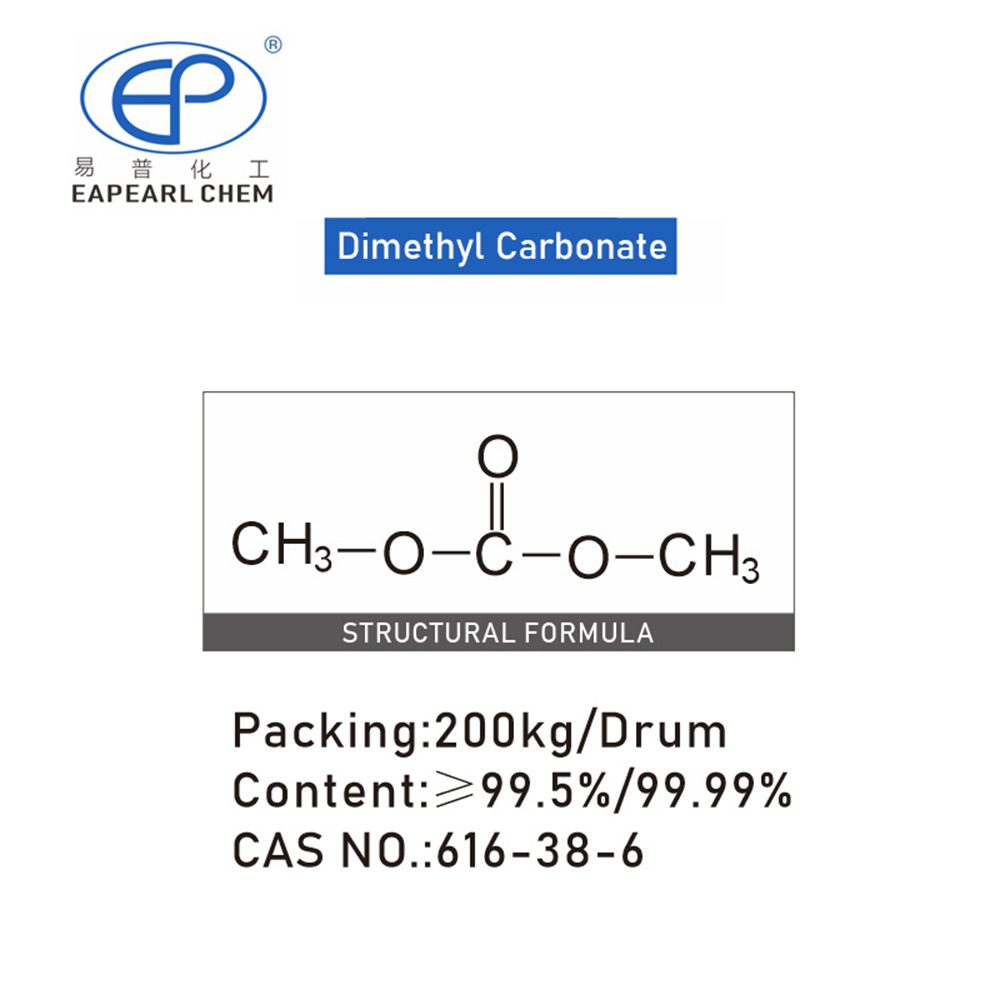

Introduction: Dimethyl carbonate, a colorless and odorless liquid, is a versatile chemical compound with diverse applications. Chemically known as dimethyl carbonate, it is characterized by its unique properties and wide-ranging utility across various industries. This mono-substituted carbonate derivative showcases a chemical structure where two methyl groups replace the hydrogen atoms in carbonate.
Synonyms: Dimethyl carbonate; Carbonic acid dimethyl ester; DMC; Methoxymethanol; Dimethyl ester of carbonic acid; Methyl carbonate; DMDC.
Nature: Dimethyl carbonate is represented by the chemical formula C3H6O3. Its molecular structure combines two methoxy groups (OCH3) with a carbonyl group (C=O). This distinctive arrangement contributes to its advantageous characteristics, including being colorless, odorless, and possessing a relatively low toxicity. With a boiling point of 90.3 °C (194.5 °F) and a melting point of -3.7 °C (25.3 °F), Dimethyl Carbonate’s physical properties make it an ideal choice for various applications.
Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) is a multifunctional, nontoxic, biodegradable reagent with tunable chemical reactivity. It is an organic compound with the chemical formula C3H6O3. It is a colorless, flammable liquid with a sweet taste. Dimethyl carbonate has a low density and can be dissolved in many organic solvents at room temperature, such as alcohols, ethers and ketones.
Dimethyl carbonate is a colorless, fast evaporating, mild non-offensive odor VOC exempt solvent with a wide range of applications. It is used in the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries, production of polycarbonates, lubricants, polyurethanes, cleaning and degreasing solvents, construction materials such as paints and adhesives, fuel additives, and in biodiesel production. It is also considered a green reagent. It is used as a methylating and carbonylating reagent in organic synthesis.
Table of Contents
Dimethyl Carbonate Packaging Information






| DMC packaging | Capacity | 20GP | 40GP |
| drum | 200 kg /drum | total 80 drums, Net 16 ton | total 128 drums, Net 25.6 ton |
| IBC drum | 800 kg /IBC | total 20 IBC, Net 16 ton | total 32 IBC, Net 25.6 ton |
| ISO Tank | 18.5 ton /ISO Tank | 1 ISO Tank, Net 18.5 ton | N/A |
For dimethyl carbonate, we welcome you to test and check the quality, if you need a sample please contact our sales team to discuss your sample requirements, we believe that our product quality is suitable for the specific application. We provide samples free of charge but the shipping cost will be borne by you.
Applications of Dimethyl Carbonate
Dimethyl Carbonate exhibits remarkable versatility, finding applications across diverse industries:
Chemical Intermediate in Pharmaceuticals:
Dimethyl Carbonate plays a crucial role as a chemical intermediate in the pharmaceutical industry. Its utility lies in esterification reactions, where it is used to synthesize key pharmaceutical compounds. By participating in the formation of esters, Dimethyl Carbonate contributes to the creation of diverse molecules that serve as building blocks for active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). The controlled and precise nature of these reactions allows for the synthesis of high-quality pharmaceutical products with defined chemical structures.


Solvent in Coatings and Adhesives:
In the realm of coatings and adhesives, Dimethyl Carbonate stands out as a versatile solvent. Its excellent solubility properties make it an ideal choice for dissolving and dispersing various components in coating formulations. As a solvent, DMC enhances the viscosity, flow, and application characteristics of coatings and adhesives. This contributes to the overall performance of the final products, ensuring uniform application and adherence to different surfaces.
Electrolyte Additive in Batteries:
Dimethyl Carbonate’s significant application in the battery industry is as an electrolyte additive in lithium-ion batteries. Its inclusion in the electrolyte formulation contributes to improved battery performance. DMC enhances the safety and stability of lithium-ion batteries, addressing issues such as thermal stability and electrolyte flammability. The use of Dimethyl Carbonate as an additive supports advancements in battery technology, promoting energy efficiency and longer battery life.




Cleaning and Degreasing Agent:
As a cleaning and degreasing agent, Dimethyl Carbonate demonstrates its effectiveness in industrial applications. Its solvent properties enable it to dissolve and remove contaminants, oils, and greases from surfaces. This makes DMC a valuable component in precision cleaning processes, particularly in industries such as electronics manufacturing, where stringent cleanliness standards are essential. The use of DMC as a cleaning agent contributes to efficient and thorough cleaning without leaving residues.
Polycarbonate Production:
Dimethyl Carbonate plays a vital role in the production of polycarbonates, high-performance thermoplastics with a wide range of applications. In the synthesis process, DMC is involved in the polymerization of monomers to form polycarbonate chains. Polycarbonates produced with Dimethyl Carbonate exhibit exceptional transparency, impact resistance, and heat resistance, making them suitable for use in items such as eyewear lenses, electronic components, and medical devices.



Pesticide Formulations:
Within the agricultural industry, Dimethyl Carbonate finds application in the formulation of certain pesticides and herbicides. Its role as a solvent in pesticide formulations ensures the even distribution and stability of active ingredients. This application enhances the efficacy of agricultural chemicals by facilitating the delivery of key components to target areas. The use of DMC in pesticide formulations aligns with the agricultural sector’s need for effective and reliable solutions in crop protection.
These detailed descriptions highlight the specific roles and benefits of dimethyl carbonate in various applications, showcasing its versatility and significance across diverse industries. If you have other specific dimethyl carbonate application questions, please contact us.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Technical of Dimethyl Carbonate
| Name | Dimethyl Carbonate |
| Synonyms | Carbonic acid dimethyl ester; DMC; Methoxymethanol; Dimethyl ester of carbonic acid; Methyl carbonate; |
| CAS | 616-38-6 |
| EINECS | 210-478-4 |
| Molecular Formula | C3H6O3 |
| Molar Mass | 90.08 |
| Density | 1.069 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| Melting Point | 2-4 °C (lit.) |
| Boling Point | 90 °C (lit.) |
| Flash Point | 65°F |
| Water Solubility | 139 g/L |
| Solubility | 139g/l |
| Vapor Presure | 18 mm Hg ( 21.1 °C) |
| Vapor Density | 3.1 (vs air) |
| Appearance | Liquid |
| Color | <50(APHA) |
| Odor | Pleasant |
| Merck | 143241 |
| BRN | 635821 |
| Storage Condition | Store below +30°C. |
| Stability | Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, potassium t-butoxide. |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Explosive Limit | 4.22-12.87%(V) |
| Refractive Index | n20/D 1.368(lit.) |
| LogP | 0.23-0.354 at 20-25℃ |
| Physical and Chemical Properties | Characteristics of colorless transparent liquid, irritating odor. properties is an important organic synthesis intermediates, molecular structure containing carbonyl, methyl and methoxy functional groups, with a variety of reaction properties, in the production of safe and convenient, characteristics of less pollution and easy transportation. |
| HS Code | 2920 90 10 |
| Toxicity | LD50 in rats (g/kg): 13.8 orally; 2.5 dermally; LC50 (4 hr) in rats (mg/l): 140 by inhalation (Ono) |
Dimethyl Carbonate Production
The production of dimethyl carbonate involves a series of steps, typically through the reaction of methanol with phosgene or carbon dioxide. Here’s a detailed description of the specific production process:
Dimethyl Carbonate Production Process:
Raw Materials:
- Methanol: The primary raw material for Dimethyl Carbonate production.
- Phosgene or Carbon Dioxide: Reactants used in the synthesis process.
Methanol Oxidation:
- The production process usually starts with the oxidation of methanol. Methanol reacts with air or oxygen in the presence of a catalyst to form formaldehyde: 2 CH3OH+O2→2 CH2O+2 H2O
Formaldehyde Esterification:
- The formaldehyde produced in the previous step undergoes esterification with methanol to form methyl formate: CH2O+CH3OH→CH3OCOH
Methyl Formate Transesterification:
- Methyl formate further reacts through transesterification with methanol in the presence of a catalyst to produce Dimethyl Carbonate: CH3OCOH+CH3OH→CH3OCOOCH3+H2O
Purification and Distillation:
- The crude Dimethyl Carbonate is then subjected to purification processes to remove impurities and by-products. Distillation is often employed to separate and collect pure Dimethyl Carbonate.
Recovery and Recycle:
- Efforts are made to recover any unreacted methanol and other components from the distillation process. This aids in minimizing waste and improving the overall efficiency of the production.
Quality Control:
- The final product undergoes quality control measures to ensure it meets specified standards. This may involve testing for purity, composition, and adherence to regulatory requirements.
Storage and Packaging:
- The purified Dimethyl Carbonate is stored under controlled conditions to maintain its quality. It is then packaged for distribution and use in various industries.
Dimethyl Carbonate Storage
Dimethyl Carbonate (DMC) is a versatile chemical compound with diverse applications, ranging from pharmaceuticals and coatings to batteries. Proper storage and environmentally responsible disposal of Dimethyl Carbonate are crucial aspects to ensure safety, compliance with regulations, and minimize environmental impact.
Storage Conditions:
Dimethyl Carbonate should be stored under controlled conditions to maintain its stability and prevent potential hazards. Key storage considerations include:
Temperature Control: Store DMC in a cool and well-ventilated area to prevent excessive temperature fluctuations. Avoid exposure to direct sunlight or heat sources.
Container Material: Utilize containers made of materials compatible with Dimethyl Carbonate, such as stainless steel or high-density polyethylene. Ensure containers are tightly sealed to prevent leaks.
Inert Gas Blanketing: In larger storage vessels, consider inert gas blanketing (e.g., nitrogen) to minimize the risk of oxidation or degradation.
Separation from Incompatible Substances: Store Dimethyl Carbonate away from incompatible substances, such as strong acids, bases, and reducing agents.
Safety Labels and Documentation: Clearly label storage containers with safety information, including hazard symbols and emergency contact details. Maintain up-to-date documentation on the quantity and condition of stored DMC.
Advantages of the Chinese Dimethyl Carbonate Market
The Chinese Dimethyl Carbonate (DMC) market has emerged as a significant player on the global stage, demonstrating a multitude of advantages that contribute to its prominence in various industries. From economic strengths to technological advancements, this page explores the key factors that make the Chinese DMC market a powerhouse in the chemical industry.
Production Capacity and Supply Chain Resilience:
China boasts a robust production capacity for Dimethyl Carbonate, ensuring a stable and abundant supply. This resilience in the supply chain has positioned China as a reliable source for DMC, meeting the increasing demands of both domestic and international markets.
Cost Competitiveness:
One of the major advantages of the Chinese DMC market is its cost competitiveness. The efficient production processes and economies of scale achieved in China contribute to cost-effectiveness, making Chinese DMC products highly attractive to industries seeking quality at a competitive price point.
Technological Advancements:
China has continually invested in research and development, fostering technological advancements in Dimethyl Carbonate production processes. These advancements not only improve efficiency but also contribute to the development of high-purity DMC variants, expanding its applications across various industries.
Growing Demand in End-Use Industries:
The Chinese Dimethyl Carbonate market has experienced a surge in demand from diverse end-use industries. From pharmaceuticals to electronics and energy storage, the versatility of DMC has fueled its adoption in numerous applications, driving the growth of the market.
Environmental Sustainability:
As global environmental concerns escalate, the environmentally friendly properties of Dimethyl Carbonate position it as a sustainable choice. The Chinese market’s focus on green chemistry and sustainable practices aligns with the growing emphasis on eco-friendly solutions, attracting environmentally conscious industries.
Government Initiatives and Policies:
China’s supportive government initiatives and policies play a pivotal role in fostering the growth of the DMC market. Strategic policies that promote chemical innovation, research, and development create a favorable environment for businesses to thrive and contribute to the global chemical landscape.
Global Export Hub:
The Chinese Dimethyl Carbonate market has evolved into a global export hub, catering to the demands of international markets. This global reach enhances China’s influence in the chemical industry and contributes to the country’s status as a key player in the global trade of Dimethyl Carbonate.
Collaborative Industry Ecosystem:
China’s DMC market benefits from a collaborative industry ecosystem, with partnerships and collaborations between manufacturers, suppliers, and research institutions. This collaborative approach fosters innovation, accelerates technological advancements, and strengthens the overall competitiveness of the market.
In conclusion, the Chinese Dimethyl Carbonate market stands out for its production prowess, cost competitiveness, technological advancements, and alignment with sustainable practices. As industries continue to seek reliable and sustainable chemical solutions, the advantages offered by the Chinese DMC market position it as a leader in the global chemical landscape, shaping the future of Dimethyl Carbonate applications worldwide.
Our Team
FAQs of Dimethyl Carbonate
A1: Dimethyl carbonate finds applications as a chemical intermediate in pharmaceuticals, a solvent in coatings and adhesives, an electrolyte additive in batteries, and more.
A2: While Dimethyl Carbonate has low toxicity, it is essential to follow safety protocols. Handling DMC requires adherence to proper safety measures, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
A3: Yes, Dimethyl Carbonate is flammable. Precautions should be taken to store and handle it away from open flames, sparks, or other potential ignition sources.
A4: Dimethyl carbonate is typically produced through the oxidation of methanol, followed by esterification and transesterification processes. The specific production methods may vary.
A5: No, Dimethyl Carbonate is a hazardous chemical, and its purchase is subject to strict regulations. Individuals must meet the necessary qualifications for purchasing and handling dangerous chemicals.
A6: To purchase Dimethyl Carbonate, individuals or entities must possess the appropriate qualifications for handling dangerous chemicals. This includes compliance with regulatory requirements, proper storage facilities, and adherence to safety protocols.
A7: Absolutely. We offer 100g-200g samples, with the client only covering shipping costs.
A8: Standard lead times are approximately 2-4 weeks, varying based on order size and destination.
A9: Our standard payment terms include a 30% advance and the balance against delivery, but terms can be negotiated for long-term partnerships.
A10: Yes, we offer comprehensive after-sales support, addressing any post-purchase queries or concerns.
A11: As a supplier, in order to provide you with an accurate quote for your product, please inform us of the quantity you require, the required purity specifications, any specific packaging needs, your shipping location, and whether your application requires any customization requirements or certifications.


