Ethyl methyl carbonate
Ethyl Methyl Carbonate: Unlocking Efficiency and Safety in Industry
Welcome to the dynamic world of Ethyl Methyl Carbonate (EMC) – a key player in modern industrial applications, particularly in the realm of lithium batteries. As a versatile solvent known for its high quality and stability, EMC is revolutionizing industries worldwide.

Introduction:
Ethyl Methyl Carbonate is a clear, colorless organic compound known for its excellent solvent properties. Represented by the chemical formula C4H8O3, EMC is used extensively in various industrial applications due to its physical and chemical characteristics.
Synonyms:
Methyl ethyl carbonate, EMC, Methylethylcarbonate, ETHYL METHYL CARBONATE, Methyl ethyl carbonate, Ethyl Methyl Carbonate, EthylMethylCarbonate(Emc), Carbonic acid methyl ethyl, Carbonic acid ethyl methyl ester;
Nature:
The chemical nature of EMC is marked by its moderate boiling point and good solvency capabilities. It is relatively stable under normal conditions but requires proper handling and storage due to its reactivity under specific circumstances.
Table of Contents
Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Packaging Information






| EMC packaging | Capacity | 20GP | 40GP |
| drum | 200 kg /drum | total 80 drums, Net 16 ton | total 128 drums, Net 25.6 ton |
| IBC drum | 800 kg /IBC | total 20 IBC, Net 16 ton | total 32 IBC, Net 25.6 ton |
| ISO Tank | 18.5 ton /ISO Tank | 1 ISO Tank, Net 18.5 ton | N/A |
For ethyl methyl carbonate, we welcome you to test and check the quality, if you need a sample please contact our sales team to discuss your sample requirements, we believe that our product quality is suitable for the specific application. We provide samples free of charge but the shipping cost will be borne by you.
Applications of Ethyl Methyl Carbonate
Ethyl Methyl Carbonate (EMC) is a versatile organic compound with a range of specific applications across various industries. Here are detailed explanations of some of its key applications:
Electrolyte Component in Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- In-Depth Detail: EMC is crucial in the battery industry, particularly for lithium-ion batteries. It’s used to create the electrolyte solution that is central to the battery’s operation. This solution contains lithium salts dissolved in a solvent mixture, often including EMC.
- Key Properties: EMC is chosen for its low viscosity, which enhances the mobility of lithium ions, and its high dielectric constant, which improves the solvation of lithium ions. These properties are essential for the battery’s energy density, charge rate, and overall performance.
- Impact on Battery Life: EMC also contributes to the thermal stability and safety of the battery, reducing the risk of overheating and extending the battery’s life.



Solvent for Organic Synthesis:
- In-Depth Detail: In organic chemistry, EMC is a preferred solvent for various synthesis reactions. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of organic compounds without participating in the reaction makes it ideal for complex organic syntheses.
- Role in Reactions: EMC is particularly useful in reactions that require precise control over the reaction environment. It does not react with reagents or intermediates, ensuring the purity of the final product.
- Environmental Aspect: As a more environmentally friendly solvent, EMC is favored in ‘green chemistry’ practices. Its use aligns with the industry’s shift towards sustainable and eco-friendly chemical processes.
Pharmaceutical Industry:
- In-Depth Detail: EMC’s role in pharmaceuticals extends beyond just being a solvent. It’s used in the synthesis of certain drug compounds and as an intermediate in various pharmaceutical formulations.
- Safety and Efficacy: Its low toxicity is crucial in pharmaceutical applications, ensuring that the drug formulations are safe for human use. EMC’s chemical stability also prevents undesirable reactions during drug storage and use.
- Versatility: Its solvent properties aid in the efficient mixing of ingredients and the creation of uniform and stable pharmaceutical products, from tablets to liquid formulations.




Flavor and Fragrance Industry:
- In-Depth Detail: In the world of flavors and fragrances, EMC is an invaluable tool. It’s used to dissolve and carry aromatic compounds in perfumes, colognes, and flavorings.
- Evaporation Characteristics: EMC’s volatility is a significant advantage. It evaporates without leaving any residue, which is essential in fragrance products where a clean and unaltered scent is desired.
- Applications: In flavorings, EMC helps in evenly distributing flavors in food products, ensuring a consistent taste experience.
Paints and Coatings Industry:
- In-Depth Detail: EMC’s role in paint and coatings is multifaceted. It’s used as a solvent to aid in pigment dispersion, improve flow properties, and adjust drying times.
- Enhancing Paint Properties: Its inclusion in paint formulations can enhance the application properties, ensuring a smooth and even coat without imperfections.
- Environmental Impact: The use of EMC can also contribute to reducing the VOC (Volatile Organic Compounds) content in paints, aligning with environmental regulations and standards.



Adhesives and Sealants:
- In-Depth Detail: In adhesives and sealants, EMC is used to modify viscosity, enhance adhesive properties, and provide flexibility to the final product.
- Improving Performance: Its inclusion can improve the spreadability of adhesives, ensuring a strong and even bond. In sealants, EMC contributes to the flexibility and durability of the seal.
- Versatile Applications: From industrial adhesives to everyday household glues, EMC plays a critical role in enhancing the performance and usability of these products.
Each of these applications demonstrates the versatility of Ethyl Methyl Carbonate, showcasing its utility in a wide range of industrial and commercial settings. The compound’s favorable chemical properties, such as low toxicity, biodegradability, and excellent solvent capabilities, make it a valuable component in many formulations and processes.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Technical of Ethyl Methyl Carbonate
| Name | Ethyl methyl carbonate |
| Synonyms | Methyl ethyl carbonate, EMC, Methylethylcarbonate, ETHYL METHYL CARBONATE, Methyl ethyl carbonate, Ethyl Methyl Carbonate, EthylMethylCarbonate(Emc), Carbonic acid methyl ethyl, Carbonic acid ethyl methyl ester; |
| CAS | 623-53-0 |
| EINECS | 208-760-7 |
| Molecular Formula | C4H8O3 |
| Molar Mass | 104.1 |
| Density | 1.006 g/mL at 25 °C |
| Melting Point | -14.5℃ |
| Boling Point | 107 °C |
| Flash Point | 23°C |
| Water Solubility | 46.8-47.1g/L at 20℃ |
| Vapor Presure | 43hPa at 25℃ |
| Appearance | clear liquid |
| Color | Colorless to Almost colorless |
| Storage Condition | 2-8°C |
| Refractive Index | n20/D 1.378 |
| Physical and Chemical Properties | Character: colorless liquid. |
| melting point -14.5 ℃ | |
| boiling point 109.2 ℃ | |
| relative density 1.002 | |
| solubility insoluble in water, soluble in ether and alcohol. | |
| HS Code | 29209090 |
| LogP | 0.972 at 40℃ |
Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Production
The synthesis of EMC typically involves the reaction of ethanol and methanol with an appropriate carbonate source. A common method for producing EMC is through the transesterification process. Here’s a general outline of the production process:
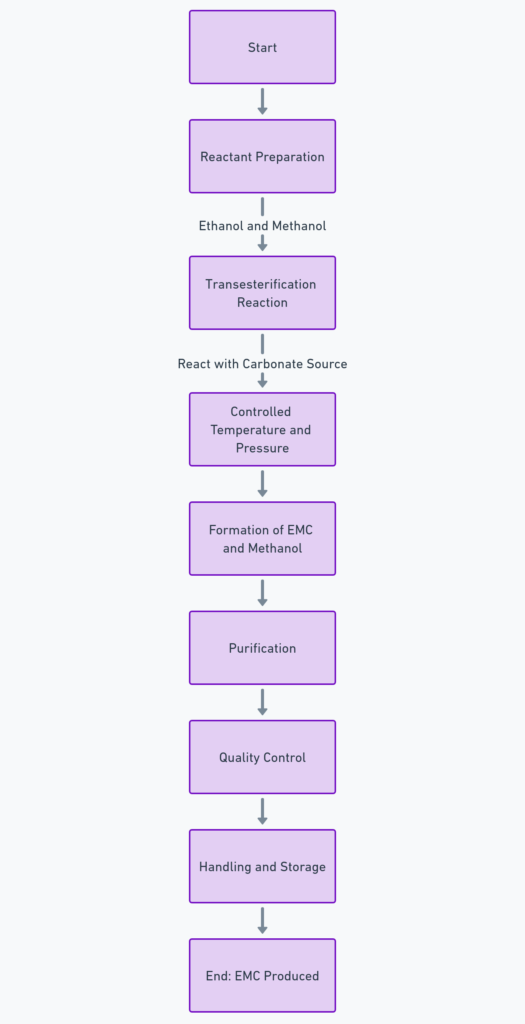

Reactant Preparation:
- Ethanol (C2H5OH) and methanol (CH3OH) are the primary reactants.
- A source of carbonate, commonly dimethyl carbonate (DMC) or diethyl carbonate (DEC), is also required.
Transesterification Reaction:
- The transesterification process involves reacting ethanol and methanol with the carbonate source (e.g., DMC or DEC).
- The reaction is typically catalyzed by a base, such as sodium methoxide, potassium carbonate, or a similar compound.
- The reaction is conducted under controlled temperature and pressure conditions, often at moderate temperatures (e.g., 60-120°C).
- The general reaction can be represented as follows: CH3OC(O)OCH3+CH3OH+C2H5OH→CH3OC(O)OC2H5+2CH3OH. Here, DMC reacts with methanol and ethanol to form EMC and an additional molecule of methanol.
Purification:
- Post-reaction, the mixture contains EMC, unreacted alcohols, and possibly side products.
- The mixture is subjected to purification steps, such as distillation, to separate EMC from other components.
- Distillation helps in obtaining EMC at a high degree of purity, crucial for applications like electrolytes in lithium batteries.
Quality Control:
- The final product is tested to ensure that it meets the required purity and quality standards.
- Typical quality control tests might include gas chromatography (GC) or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to determine the composition and purity.
Handling and Storage:
- EMC, being a solvent, should be handled with care, including appropriate measures for storage, handling, and disposal.
- It should be stored in a cool, dry place and in a manner that prevents moisture ingress and minimizes exposure to air.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
The Dangers of Ethyl Methyl Carbonate
Ethyl Methyl Carbonate (EMC) is an organic compound with various industrial applications, notably in lithium battery production and as a solvent in pharmaceuticals. While EMC is valuable in these sectors, it also poses several risks and dangers that must be carefully managed. Understanding these hazards is crucial for ensuring safe handling and usage.
Health Hazards
Inhalation
- Respiratory Irritation: EMC vapors can irritate the respiratory tract if inhaled, causing coughing, shortness of breath, and discomfort.
- Central Nervous System Effects: High concentrations of EMC vapors can affect the central nervous system, potentially leading to headaches, dizziness, and in extreme cases, unconsciousness.
Skin Contact
- Irritation: Direct contact with EMC can cause skin irritation, leading to redness and itching.
- Dermatitis: Repeated or prolonged skin exposure may result in dermatitis.
Eye Contact
- Irritation: EMC can cause severe eye irritation, resulting in pain, redness, and tearing.
Ingestion
- Ingestion of EMC can cause gastrointestinal irritation, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Fire and Explosion Hazards
- Flammability: EMC is a flammable liquid and vapor, posing a significant risk of fire and explosion, especially in areas with poor ventilation.
- Reactivity: It can react with oxidizing agents, acids, and bases, potentially leading to hazardous reactions.
Environmental Hazards
- Ecotoxicity: EMC can be toxic to aquatic organisms, potentially causing long-term adverse effects in aquatic environments.
- VOC Emissions: As a volatile organic compound, EMC contributes to air pollution and may participate in atmospheric photochemical reactions.
Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Storage
Ethyl Methyl Carbonate (EMC) is an organic compound commonly used in various industrial and chemical applications, including as a solvent and as an electrolyte component in lithium batteries. Proper storage and disposal of EMC are critical due to its chemical properties and potential environmental impact.
EMC should be stored in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The recommended storage temperature should be maintained below room temperature, typically in the range of 15-25°C. Prolonged exposure to higher temperatures may lead to decomposition or degradation of the compound.
Container Specifications
EMC is usually stored in stainless steel or aluminum containers that are resistant to corrosion. The containers should be airtight to prevent moisture ingress and minimize exposure to air, as EMC is hygroscopic and can absorb moisture from the air.
Safety Measures
- Storage areas should be equipped with appropriate fire-fighting equipment, as EMC is flammable.
- Containers should be grounded and bonded to prevent static discharge.
- Personnel handling EMC must use proper personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and respiratory protection if necessary.
- Spill containment measures should be in place to manage accidental releases.
Advantages of the Chinese Ethyl Methyl Carbonate Market
The Chinese market for Ethyl Methyl Carbonate (EMC) has shown significant growth and development in recent years. EMC is a valuable organic compound widely used in various applications, such as solvents in pharmaceuticals, and as an electrolyte component in lithium batteries. The growth of the Chinese EMC market is attributed to several factors, making it a key player in the global landscape.
Growth Drivers of the EMC Market in China
China’s EMC market has expanded due to its burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) industry, increasing demand for high-performance batteries, and the growth of the pharmaceutical sector. Additionally, China’s focus on renewable energy has spurred the demand for efficient energy storage solutions, where EMC plays a crucial role.
Advantages of the Chinese EMC Market
Robust Manufacturing Base
China has a strong manufacturing infrastructure, capable of producing EMC at a large scale. This capacity enables China to meet both domestic and global demand efficiently.
Advancements in Research and Development
Chinese companies and research institutions have made significant strides in improving the production process of EMC, focusing on cost-effectiveness and environmental sustainability.
Government Support and Regulations
The Chinese government has provided support to the EMC industry through favorable policies, subsidies, and investments, particularly in the sectors of electric vehicles and renewable energy.
Growing Demand in Domestic Industries
The rapid growth of industries that use EMC, such as the EV sector and portable electronics, has created a substantial domestic market, fostering the growth of the EMC industry.
Export Potential
China’s ability to produce EMC cost-effectively allows it to be a major exporter, catering to the global demand, particularly in Asia, Europe, and North America.
Competitive Pricing
The scale of production and efficient manufacturing processes in China contribute to competitive pricing of EMC, making it attractive in both domestic and international markets.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the market is growing, challenges such as environmental concerns, the need for technological advancements, and international trade dynamics need to be addressed. The future outlook remains positive, with continued growth expected in the Chinese EMC market.
Our Team
FAQs of Ethyl Methyl Carbonate
A1: EMC is widely used in the production of lithium batteries, pharmaceuticals, and as a high-purity solvent in various chemical processes.
A2:
To purchase EMC, an entity must:
- Be licensed to handle and store hazardous chemicals.
- Comply with local and national regulations regarding the storage, handling, and disposal of hazardous materials.
- Have trained personnel and appropriate facilities for safe handling of EMC.
A3: EMC should be stored in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from heat and ignition sources. It must be kept in containers that are airtight to prevent moisture ingress and minimize exposure to air.
A4:
Safety measures include:
- Using personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and goggles.
- Ensuring proper ventilation in the handling area.
- Having spill containment measures and fire-fighting equipment readily available.
A5: EMC is a volatile organic compound (VOC) and can contribute to air pollution. It is also moderately toxic to aquatic life. Appropriate measures must be taken to prevent its release into the environment.
A6: Yes, EMC can be shipped internationally, provided it complies with international transport regulations for hazardous materials, including proper labeling, packaging, and documentation.
A7: Absolutely. We offer 100g-200g samples, with the client only covering shipping costs.
A8: Standard lead times are approximately 2-4 weeks, varying based on order size and destination.
A9: Our standard payment terms include a 30% advance and the balance against delivery, but terms can be negotiated for long-term partnerships.
A10: Yes, we offer comprehensive after-sales support, addressing any post-purchase queries or concerns.
A11: As a supplier, in order to provide you with an accurate quote for your product, please inform us of the quantity you require, the required purity specifications, any specific packaging needs, your shipping location, and whether your application requires any customization requirements or certifications.


