Toluene
Discover High-Quality Toluene – The Solvent Solution for Your Industry Needs
Experience the Perfect Blend of Quality, Compliance, and Cost-Effectiveness with Eapearl Toluene
What Toluene Is

Introduction
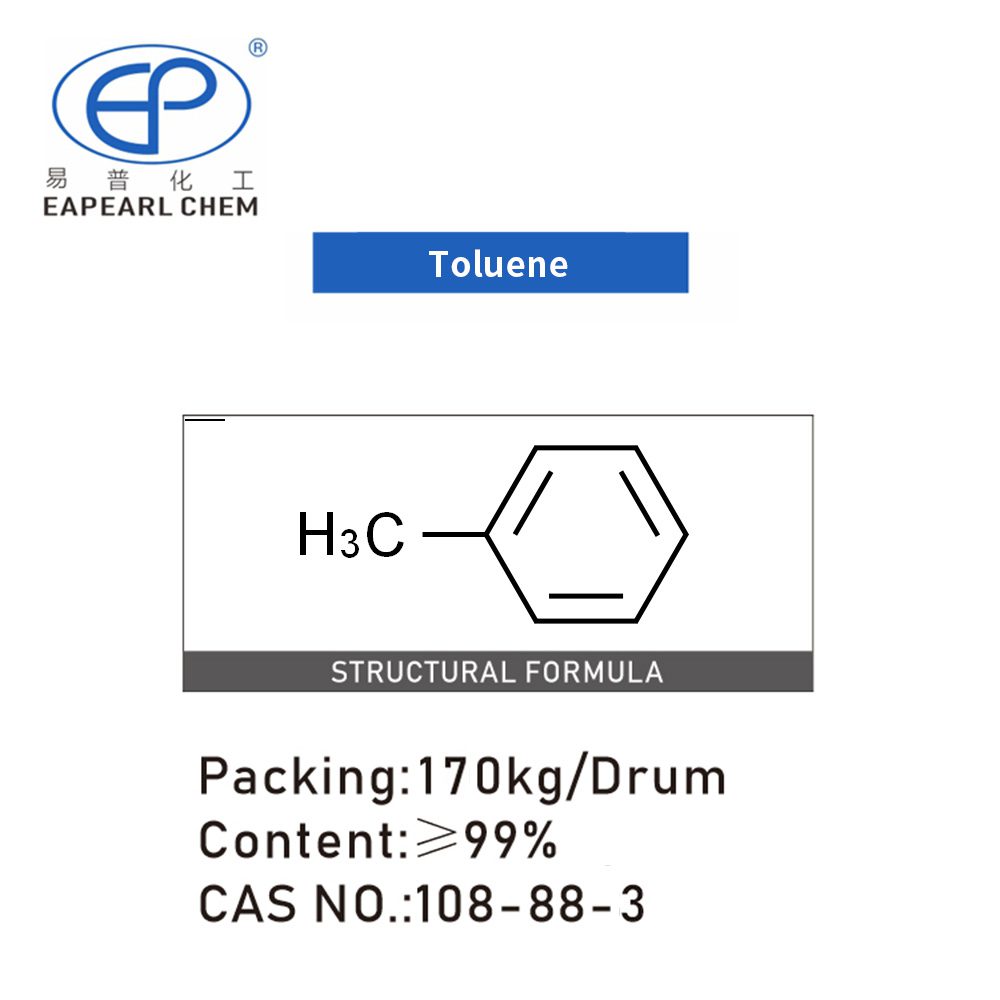
Toluene, a colorless, water-insoluble liquid, possesses a distinctive smell reminiscent of paint thinners. Chemically known as methylbenzene or phenylmethane, toluene is a mono-substituted benzene derivative, where a single methyl group replaces one hydrogen atom.
Synonyms:
Benzene,methyl-;Methylbenzene;Methacide;Methylbenzol;Phenylmethane;Toluol;Antisal 1a;CP 25;1-Methylbenzene;CP 25 (solvent);NSC 406333;1053657-77-4;1202864-97-8
Nature
Toluene is characterized by its chemical formula, C7H8. Its molecular structure consists of a benzene ring (C6H6) bonded to a methyl group (CH3), contributing to its hydrophobic nature and volatility. With a boiling point of 110.6 °C (231.1 °F) and a melting point of −95 °C (−139 °F), toluene’s physical properties enable its widespread use as a solvent.
Toluene Packaging Information


Metal Drum


IBC Drum


ISO Tank
| Toluene Packaging | Capacity | 20GP | 40GP |
| drum | 170 kg /drum | total 80 drums, Net 13.6 ton | total 120 drums, Net 20.4 ton |
| IBC drum | 1000 kg /IBC | total 20 IBC, Net 20 ton | total 24 IBC, Net 24 ton |
| ISO Tank | 23 ton /ISO Tank | 1 ISO Tank, Net 23 ton | N/A |
For Toluene, we welcome you to test and check the quality, if you need a sample please contact our sales team to discuss your sample requirements, we believe that our product quality is suitable for the specific application. We provide samples free of charge but the shipping cost will be borne by you.
What Toluene Applications


Solvent in Paints and Coatings
Toluene’s primary role in the paint industry is as a solvent and thinner. It efficiently breaks down the resins and binders in paint formulations, enhancing the consistency and application properties. Toluene’s rapid evaporation rate is critical in drying, which leaves a smooth, durable finish without affecting the color quality. It’s beneficial in high-performance coatings, such as those used in automotive and industrial settings, where a resilient finish is critical.
Adhesive Production
Toluene’s solvent action dissolves the polymers and resins that give adhesives their sticky properties. It is an essential component in the formulation of adhesives for PVC plastics, providing the necessary viscosity for easy application. As the toluene evaporates after the glue is applied, it leaves behind a strong bond resistant to moisture and temperature variations, making it ideal for household and industrial use.



Printing Industry
In the printing industry, toluene is appreciated for its fast-drying properties, which help to prevent the printed material from smudging or running. This property is particularly advantageous in high-speed printing operations. Additionally, toluene helps to maintain the integrity of the inks, ensuring they do not clog the printing presses and that the colors remain vibrant over time.
Pharmaceutical Synthesis
The synthesis of certain pharmaceuticals can involve complex chemical reactions where toluene is used as a solvent. Its stability under reaction conditions and ability to dissolve many substances make it a solvent of choice for many syntheses. Moreover, its relatively easy removal post-reaction is beneficial in the purification stages of drug manufacturing.



Production of Foam and Plastic
In plastic manufacturing, toluene is a precursor in the synthesis of TDI, which is essential for producing flexible polyurethane foams. These foams are ubiquitous and found in mattresses, upholstery, and automotive interiors. Toluene-derived materials contribute significantly to the versatility and comfort of modern foam-based products.
Additive in Race Fuels
Toluene is sometimes used as an additive in race fuels to elevate octane levels, thereby enhancing combustion efficiency and power output. It allows for higher compression ratios and more aggressive engine tuning, which can translate to better performance on the racetrack. However, this use is controversial and regulated due to the environmental impact and health risks associated with toluene emissions.




Production of Explosives
Toluene is nitrated to produce TNT, an explosive compound with a long history of military and civil engineering applications. The nitration process involves chemical reactions that introduce nitro groups into the toluene molecule, significantly altering its chemical stability and making it explosive upon impact or when ignited.
Leather Tanning
Toluene’s degreasing properties are crucial in preparing hides in the leather tanning industry. It cleanses the raw hides, removing natural fats and oils to ensure an even absorption of tanning agents. Additionally, in dyeing processes, toluene-based solvents can help to achieve uniform coloration and enhance the penetration and fixation of dyes.




Nail Polish and Cosmetics
Toluene ensures a smooth and durable finish in nail polishes, acting as a solvent that uniformly disperses the pigment and assists in forming a quick-drying film. In cosmetics, its application extends to creating transparent, vibrant colors and ensuring the products have a pleasing consistency. However, due to potential health impacts, its use in cosmetics is increasingly replaced by safer alternatives.
toluene’s
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Toluene production
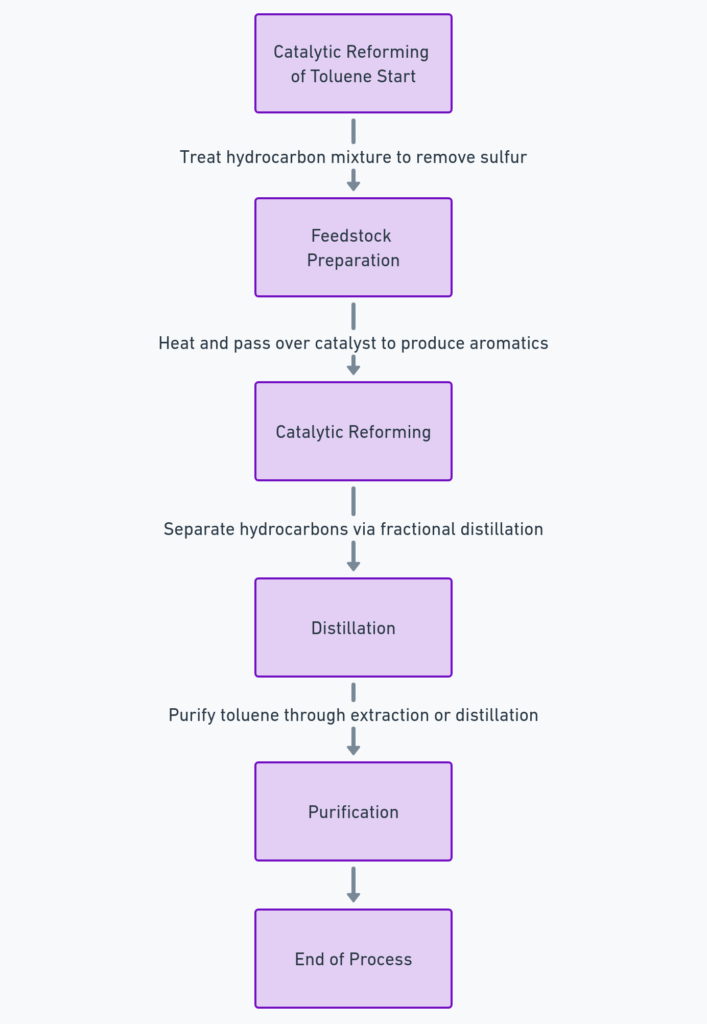

Catalytic Reforming
This is the most common method for producing toluene commercially. The process involves:
- Feedstock Preparation: The feedstock, typically a mixture of hydrocarbons from petroleum, is treated to remove sulfur compounds that can poison the catalysts used in the reforming process.
- Catalytic Reforming: The treated feedstock is heated and passed over a platinum or rhenium catalyst at high temperatures and pressures. This catalytic reaction rearranges the hydrocarbon molecules to produce aromatics, including benzene, toluene, and xylenes (BTX).
- Distillation: The output from the catalytic reforming is a mixture of various hydrocarbons, which are then separated using fractional distillation. The aromatics are extracted based on their boiling points, with toluene usually distilling between benzene and xylene.
- Purification: Toluene can be purified through extraction, azeotropic or extractive distillation, or hydrotreating to remove any residual sulfur compounds or unsaturated hydrocarbons.
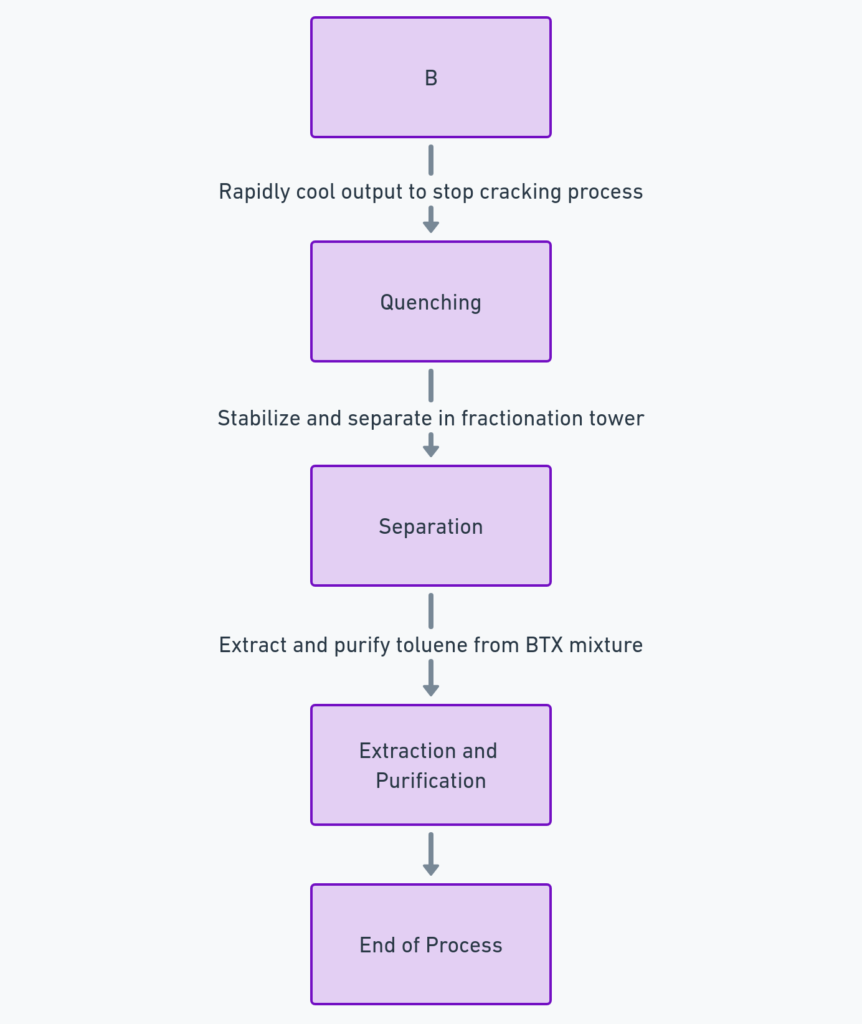

Pyrolysis Gasoline (Pygas) Production
Pygas is a by-product of the naphtha cracking process of producing ethylene and propylene. Toluene production from pages includes:
- Thermal Cracking: Naphtha feedstock is thermally cracked in a steam cracker or pyrolysis furnace at high temperatures to produce olefins and aromatics.
- Quenching: The output from the cracker is rapidly cooled or ‘quenched’ to stop the cracking process. This produces a complex mixture of hydrocarbons, including pyrolysis gasoline.
- Separation: The pyrolysis gasoline is stabilized and then sent to a fractionation tower, separated into various cuts. The BTX aromatics are isolated from the other hydrocarbons.
- Extraction and Purification: Like catalytic reforming, the BTX mixture is subjected to extraction and distillation processes to separate and purify toluene to the desired purity levels for industrial use.
How can we handle your order?


step 1
We will communicate with you within 24 hours after you send an enquiry.


step 2
If you need sample testing, we will send samples within 5 days,≤50kg, Express delivery recommended, usually called as DDU service; delivery time 5-7 days. Door to door service.


step 3
If you need bulk goods after the sample test is qualified, we will ship the goods to the port and keep the samples within 6 days after the order is confirmed. Sea shipping recommended, usually called as FOB, CFR, or CIF service.delivery time 10-45 days. Port to port service.


step 4
After waiting for you to receive the goods, we will arrange professional staff to pay a return visit within 7 days.
REQUEST A QUOTE FOR MORE DETAILS
Toluene Technical Data
| Name | Toluene |
| Molecular Formula | C7H8 |
| Molar Mass | 92.14 |
| Density | 0.8636 g/cm3 @ Temp: 20 °C |
| Melting Point | -94.9 °C |
| Boling Point | 110.6 °C |
| Water Solubility | H2O: 0.5 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Appearance | Toluene appears as a clear, colorless liquid with a characteristic aromatic odor. Flashpoint 40°F. Less dense than water (7.2 lb/gal) and insoluble in water. Hence, it floats on water. Vapors heavier than air. It may be toxic by inhalation, ingestion, or skin contact. Used in aviation and automotive fuels, as a solvent, and to make other chemicals. |
| Specific Gravity | 92.14 |
| Color | colorless |
| Odor | Sweet, pungent, benzene-like odor |
| Storage Condition | 0-6°C |
| Stability | Stable under recommended storage conditions. |
Qualifications and Documents of Sodium Nitrate
Toluene Storage and Environmental Disposal
Toluene is an organic solvent known for its wide range of industrial applications. Proper storage and disposal of toluene are critical due to its flammability, volatility, and potential adverse health and environmental impacts.
Storage of Toluene
Safety Measures
Toluene should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from any ignition source, as it emits vapors that can form explosive mixtures with air. It is recommended to store toluene in a designated flammable liquid storage cabinet. These cabinets are typically constructed from materials that can withstand high temperatures and are designed to contain spills.
Container Specifications
The solvent should be kept in tightly closed containers of materials compatible with toluene, such as stainless steel or certain types of plastic like HDPE (high-density polyethylene). The containers should contain the chemical’s identity, hazard warnings, and manufacturer’s information.
Secondary Containment
As an additional precaution, secondary containment systems, such as spill pallets or containment berms, should be used to catch and hold any accidental releases. This protects against soil and water contamination.
Environmental Disposal of Toluene
Regulations
Disposal of toluene must adhere to local, state, and federal regulations. For instance, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) categorizes toluene as hazardous waste. Thus, it must be disposed of by the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA).
Disposal Methods
1. Incineration: Toluene can be disposed of at a licensed facility through high-temperature incineration. This process breaks down the chemical into carbon dioxide and water, significantly reducing its potential impact on the environment.
2. Recycling and Recovery: Toluene can often be recovered and purified for reuse through distillation. Recycling reduces the need for disposal and the demand for fresh solvents.
3. Chemical Treatment: Toluene can be subjected to chemical treatment processes that neutralize its hazardous components. This method usually involves converting toluene into less harmful substances before disposal.
4. Biological Treatment: Certain microorganisms can metabolize toluene, and bioremediation can effectively treat contaminated soils and water. This method uses naturally occurring or genetically engineered bacteria to break down toluene.
Safety Precautions
During disposal, individuals must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and respirators to avoid exposure to toluene vapors.
Environmental Impact
Volatile Organic Compound (VOC)
Toluene is classified as a VOC and contributes to ground-level ozone and smog formation. The environmental release of toluene, whether through evaporation during storage or improper disposal, can significantly negatively impact air quality.
Water and Soil Contamination
Spills or leaks can contaminate water sources and soil, adversely affecting aquatic life and potentially entering the human food chain.
Preventive Actions
Facilities handling toluene must have spill-response plans and emergency procedures to mitigate environmental risks. Regular training for personnel and routine inspections of storage containers and areas are also crucial.
Conclusion
The proper storage and disposal of toluene are integral to environmental protection and occupational safety. By adhering to best practices and regulatory requirements, the risks associated with this chemical can be effectively managed.
Advantages of the Chinese Toluene Market
China’s chemical industry has experienced significant growth and transformation in recent decades. Toluene, a valuable aromatic hydrocarbon used in many applications, is one of the many chemicals where China has made substantial market advancements. Here are several advantages of the Chinese toluene market:
Abundant Production
Thanks to its well-established petrochemical industry, China has a large-scale production capacity for toluene. The country’s numerous chemical plants have modern technology for efficient toluene production. This abundant production meets not only domestic demands but also positions China as a significant exporter in the global market.
Vertical Integration
Many Chinese toluene producers are vertically integrated with upstream oil refineries and downstream chemical processing plants. This integration allows for cost savings, more stable supply chains, and the ability to rapidly adjust to market demands, giving China a competitive edge over countries that rely on imports for raw materials.
Strategic Global Trade
China’s strategic placement in the Asia-Pacific region, a pivotal area in international chemical trade, provides access to key export markets. China’s Belt and Road Initiative has further expanded its trade routes, enhancing its global distribution capabilities for toluene.
Government Support
The Chinese government has historically supported the petrochemical sector through subsidies, favorable policies, and investment in infrastructure. This support has bolstered the growth of the toluene market and fostered a suitable environment for continuous development.
Advanced Research and Innovation
China places a strong emphasis on research and development in the chemical industry. This focus has led to innovative production methods for toluene, which are more efficient and environmentally friendly. Chinese companies continually seek ways to improve toluene yields and reduce production costs.
Diversified Application Segments
The Chinese market benefits from a diversified application portfolio for toluene, ranging from its use in the production of benzene and xylene to serving as a solvent in paints, coatings, and adhesives. The application’s versatility ensures a steady demand within various sectors, contributing to the market’s stability.
Competitive Pricing
Chinese toluene is often competitively priced. The efficient production processes and economies of scale allow Chinese manufacturers to offer toluene at lower prices than many of their international counterparts.
Environmental Regulations
In response to global environmental concerns, China is improving its environmental policies, which include regulating the toluene industry to ensure safer production and disposal practices. This move towards sustainability can enhance the market’s reputation on the international stage.
Robust Internal Market
China’s massive industrial base provides a robust internal market for toluene. As the country grows industrially, the demand for toluene in manufacturing also increases, ensuring a solid and stable domestic market.
Conclusion
The Chinese toluene market’s advantages are multifaceted, stemming from its large-scale production, strategic trade positioning, government support, and innovative advancements. These strengths satisfy domestic demand and make China a key player in the global toluene market, capable of influencing supply dynamics and price points internationally.
Toluene FAQs
Toluene, also known as methylbenzene, is a clear, colorless liquid with a distinct smell. It is a solvent widely used in manufacturing paints, adhesives, and other industrial products.
Toluene is used in the production of benzene and xylene, as a solvent in paints, coatings, and adhesives, and in the pharmaceutical and petrochemical industries. It also manufactures foams, explosives, and certain consumer goods.
Purchasing Qualification:
1. Legal Requirements: It must comply with legal requirements for handling and purchasing dangerous chemicals.
2. License Verification: Ensure you have the appropriate license or permit to handle and purchase toluene, which is classified as hazardous.
3. Supplier Compliance: Verify that your supplier adheres to safety and environmental regulations in the production and distribution of toluene.
Safety and Handling:
1. Storage Conditions: Toluene should be stored in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from heat or ignition sources.
2. Safety Equipment: When handling toluene, use appropriate safety equipment, including gloves and goggles.
3. Spill Management: Have a spill management plan, as toluene can harm the environment and health if not managed properly.
Toluene is transported as a hazardous material. It requires specialized containers and adherence to safety protocols for transportation, including proper labeling and documentation as per regulatory standards.
Yes, toluene can often be recovered and recycled. Recycling involves distillation to purify the toluene for reuse, reducing the need for disposal and the production of new material.
Exposure to toluene can cause respiratory issues, skin irritation, and neurological effects. Long-term exposure can lead to more severe health problems, especially in high concentrations. Handling toluene in well-ventilated areas and using personal protective equipment is crucial.
Toluene should be disposed of as hazardous waste. This involves either incineration at licensed facilities or chemical treatment to neutralize its dangerous components. Always follow local and federal regulations for the disposal of hazardous materials.
Yes, toluene is regulated due to its classification as a hazardous substance. Regulations cover its production, handling, transportation, storage, and disposal to ensure safety and environmental protection.












